Pelvic Health 101
Providing you with a detailed glossary about all things pelvic health.
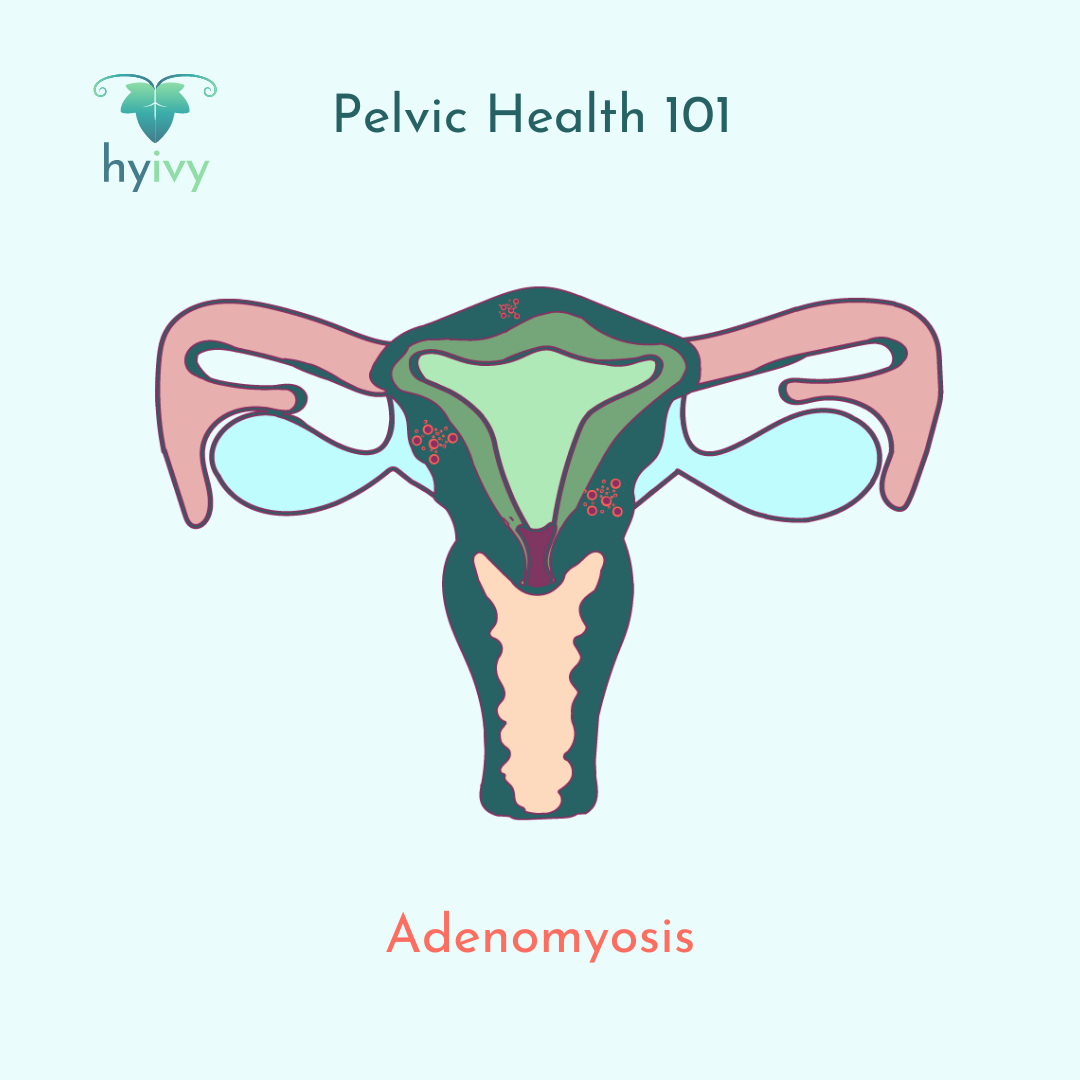
Adenomyosis is a chronic condition where the endometrial tissue from the lining of the uterus (womb) starts to grow in the muscular lining of the uterus where it does not belong. Once embedded in part or within the entire uterus wall, this tissue continues to function normally by thickening, breaking down, and bleeding during each menstrual cycle. This can cause an array of symptoms including very heavy periods that last longer than usual, severe period pain, a feeling of pressure in your abdomen, and bloating.
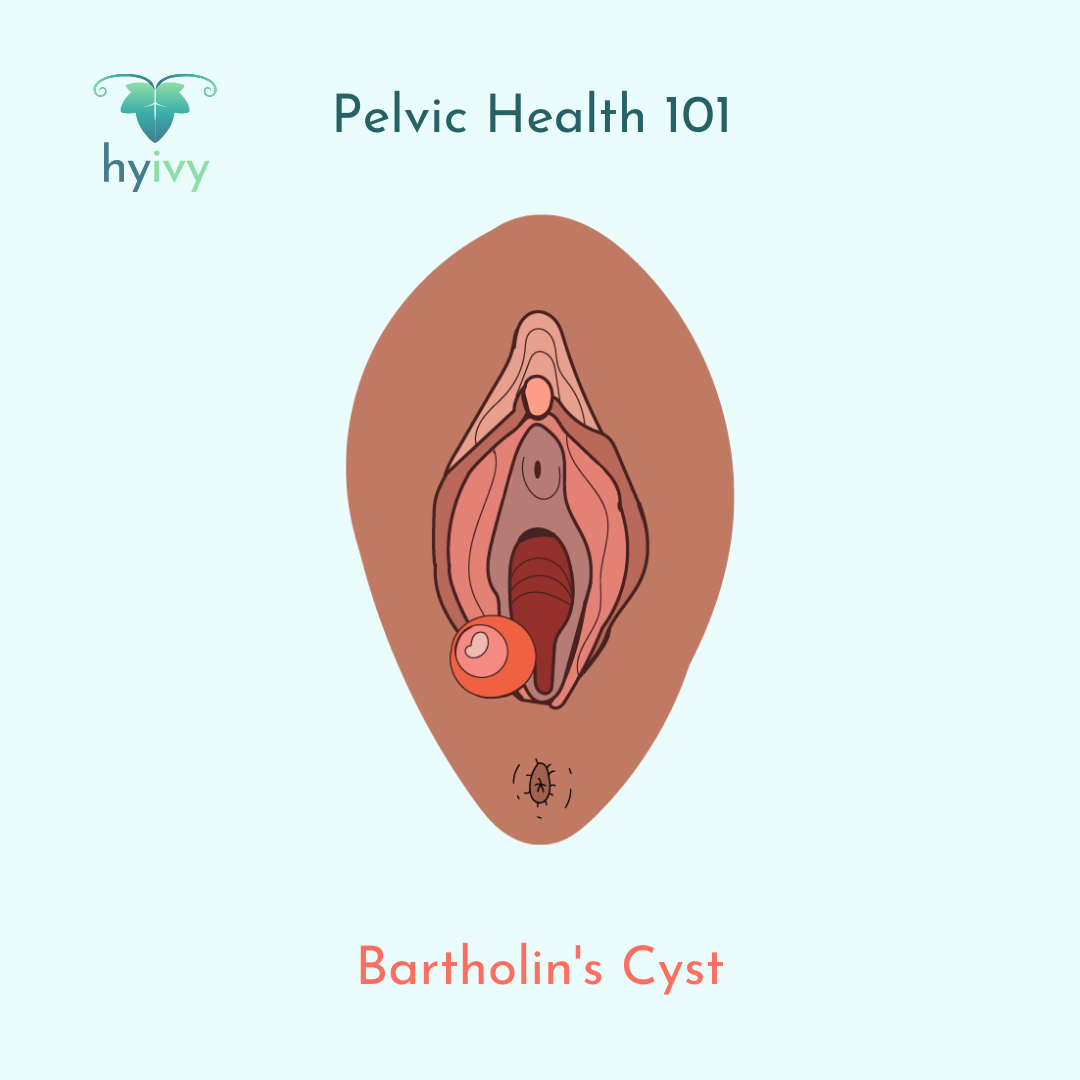
Bartholin’s glands are pea sized glands situated on either side of the vagina. They secret fluid through ducts to help to provide lubrication to the vagina. A Bartholin’s cyst, also called a Bartholin glands cyst is when the duct of these glands becomes blocked, and fluid backs up causing a cyst. Sometimes this can cause pain and irritation or become infected, requiring medical attention, or they can resolve themselves over time.
Biofeedback is a training technique that enables an individual to gain some element of voluntary control over muscular or autonomic nervous system functions using a device that produces auditory or visual stimuli. Traditional biofeedback for the pelvic floor is performed in a clinical setting where probes or sensors are used to assess pelvic floor muscle function, which is shown on a graph or as a score on a computer screen.
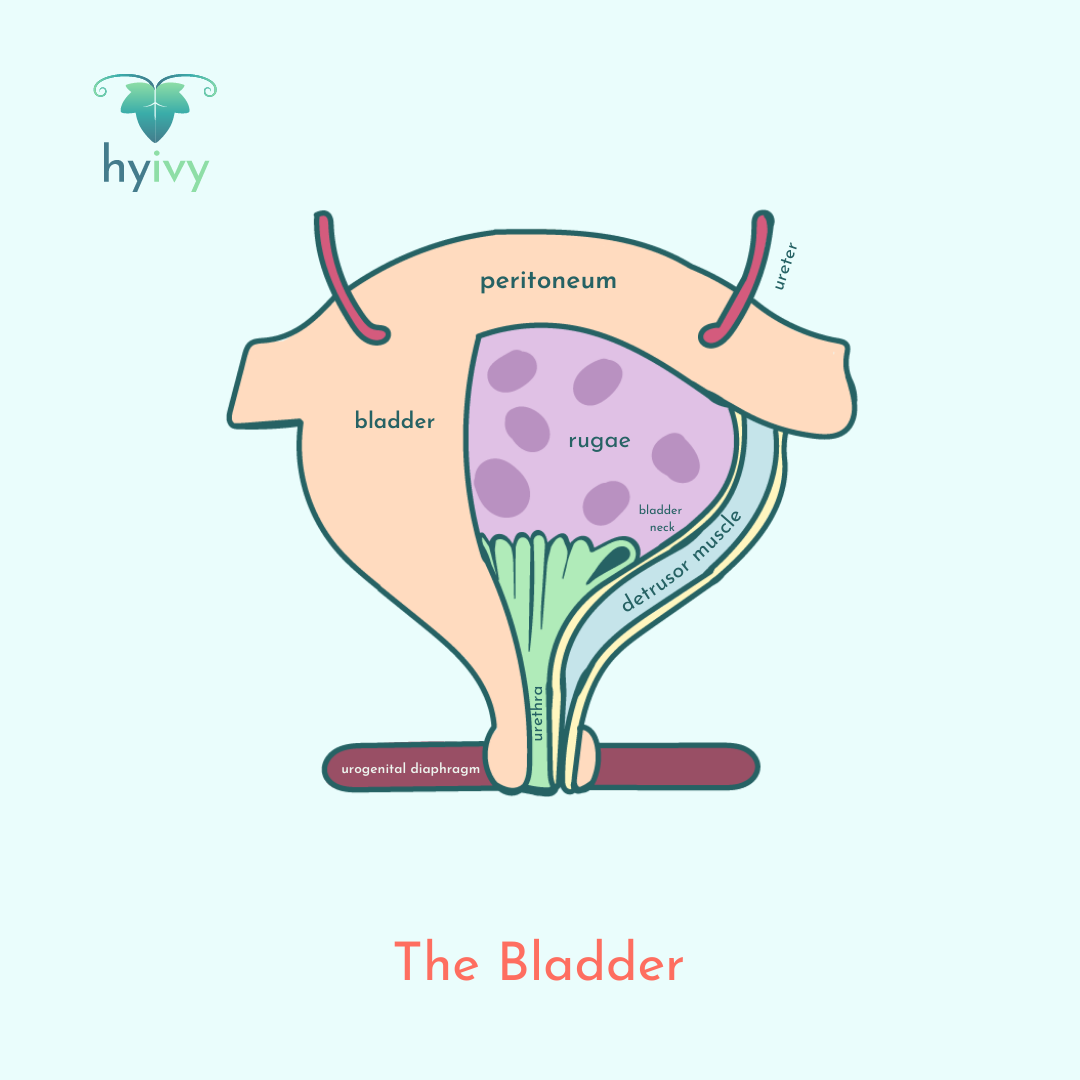
Your bladder is a triangle shaped organ responsible for temporarily storing urine that is then passed through your urethra. When you urinate, muscles in your bladder tighten and the sphincter muscles in your urethra relax, allowing urine to flow out of your body.
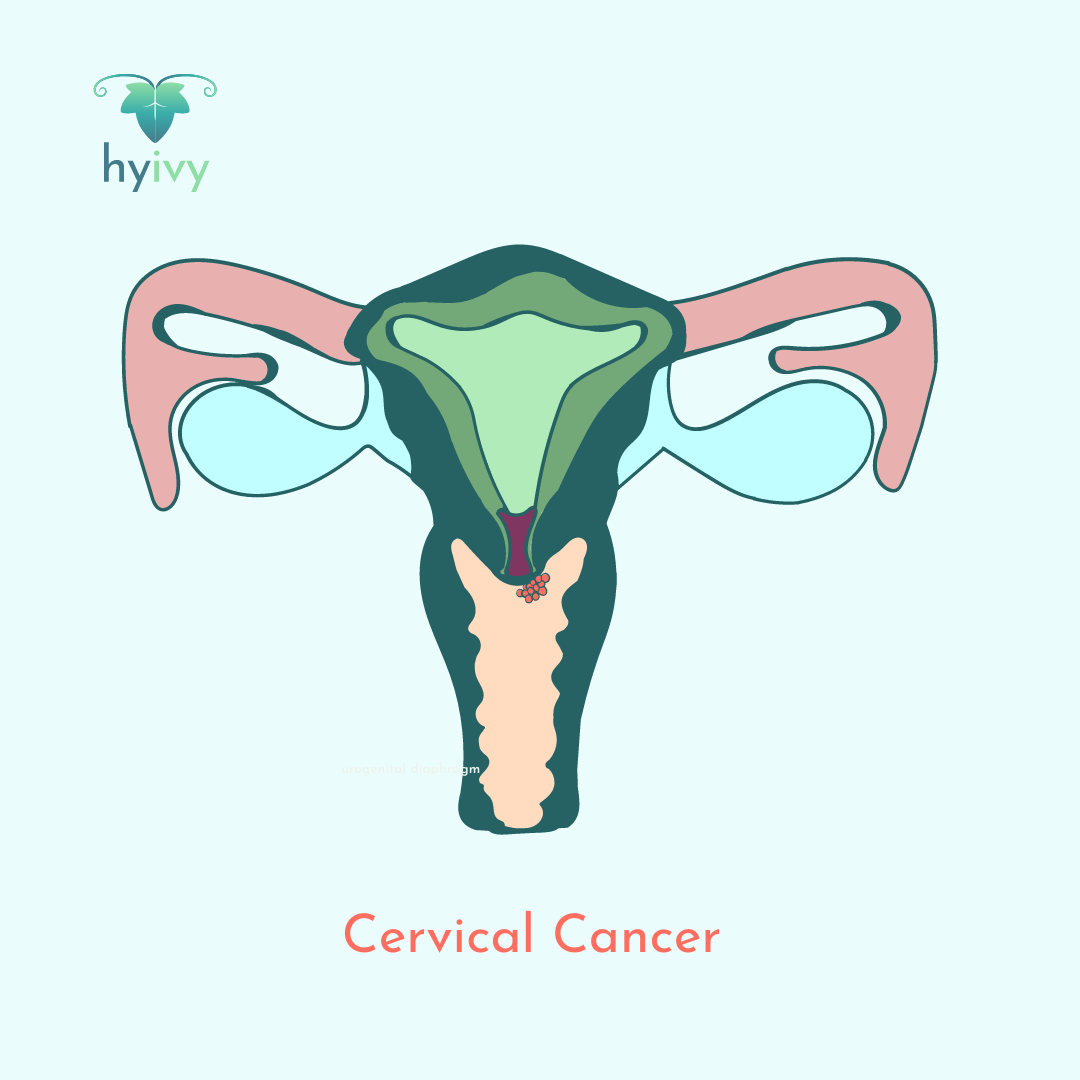
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix — the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Regular screening and an HPV (human papillomavirus) vaccine may help some reduce their risk of developing cervical cancer. Some common signs and symptoms of cervical cancer include: vaginal bleeding between periods, after menopause, or with intercourse, watery, bloody, or foul-smelling vaginal discharge, and/or pelvic pain, or pain during sex.
Chronic constipation is a condition in which infrequent bowel movements or difficulty passing stools lasts for several weeks or months. Constipation is often described as having fewer than three bowel movements a week.
 Chronic pelvic pain is pain that lasts for more than six months in the pelvic area. This pain can be experienced constantly, on a regular cycle, or only at certain times; for example: when menstruating, emptying the bladder, or having sexual intercourse.
Chronic pelvic pain is pain that lasts for more than six months in the pelvic area. This pain can be experienced constantly, on a regular cycle, or only at certain times; for example: when menstruating, emptying the bladder, or having sexual intercourse.
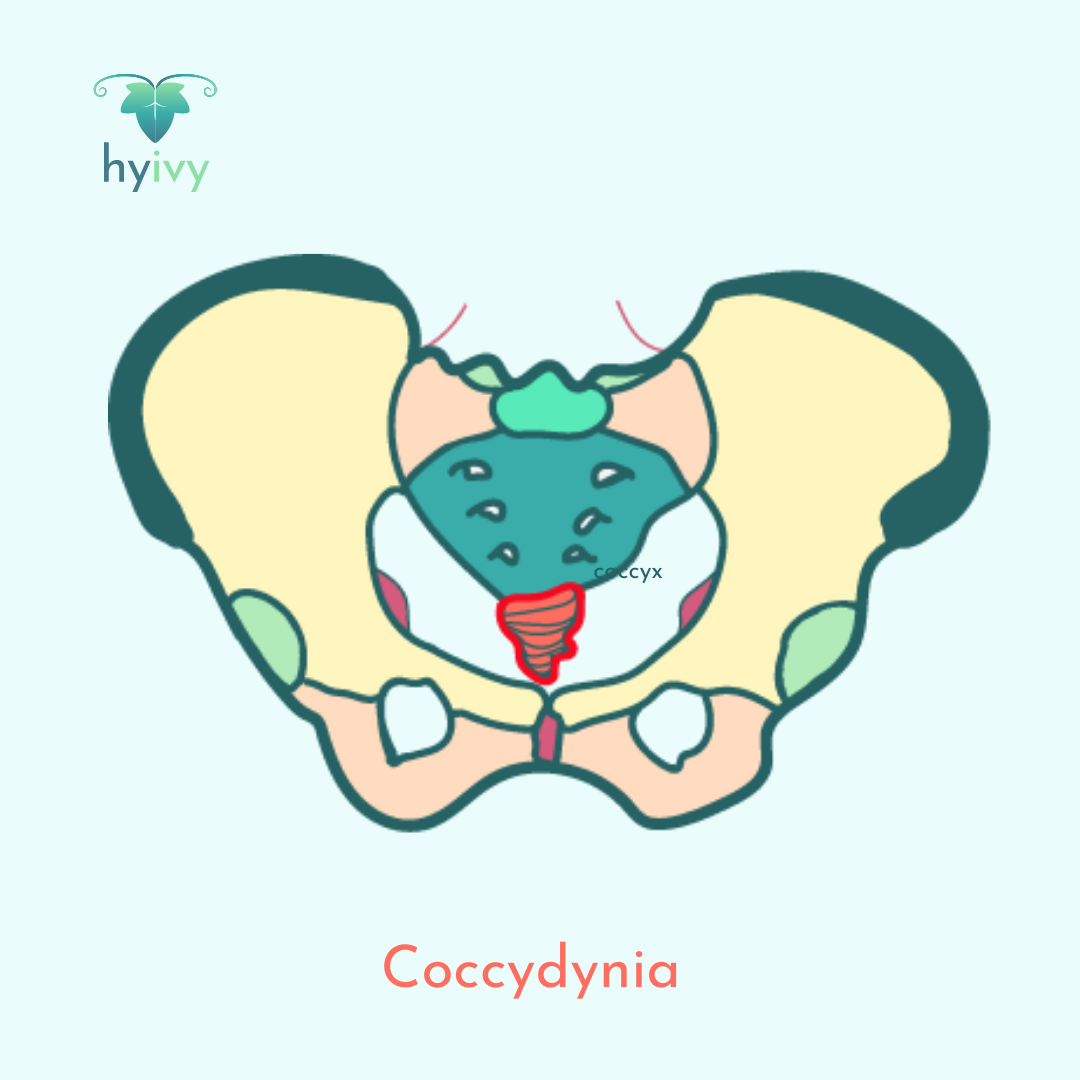 Coccydynia is pain in and around the coccyx (tail bone), a small triangular bone at the base of the spine.
Coccydynia is pain in and around the coccyx (tail bone), a small triangular bone at the base of the spine.
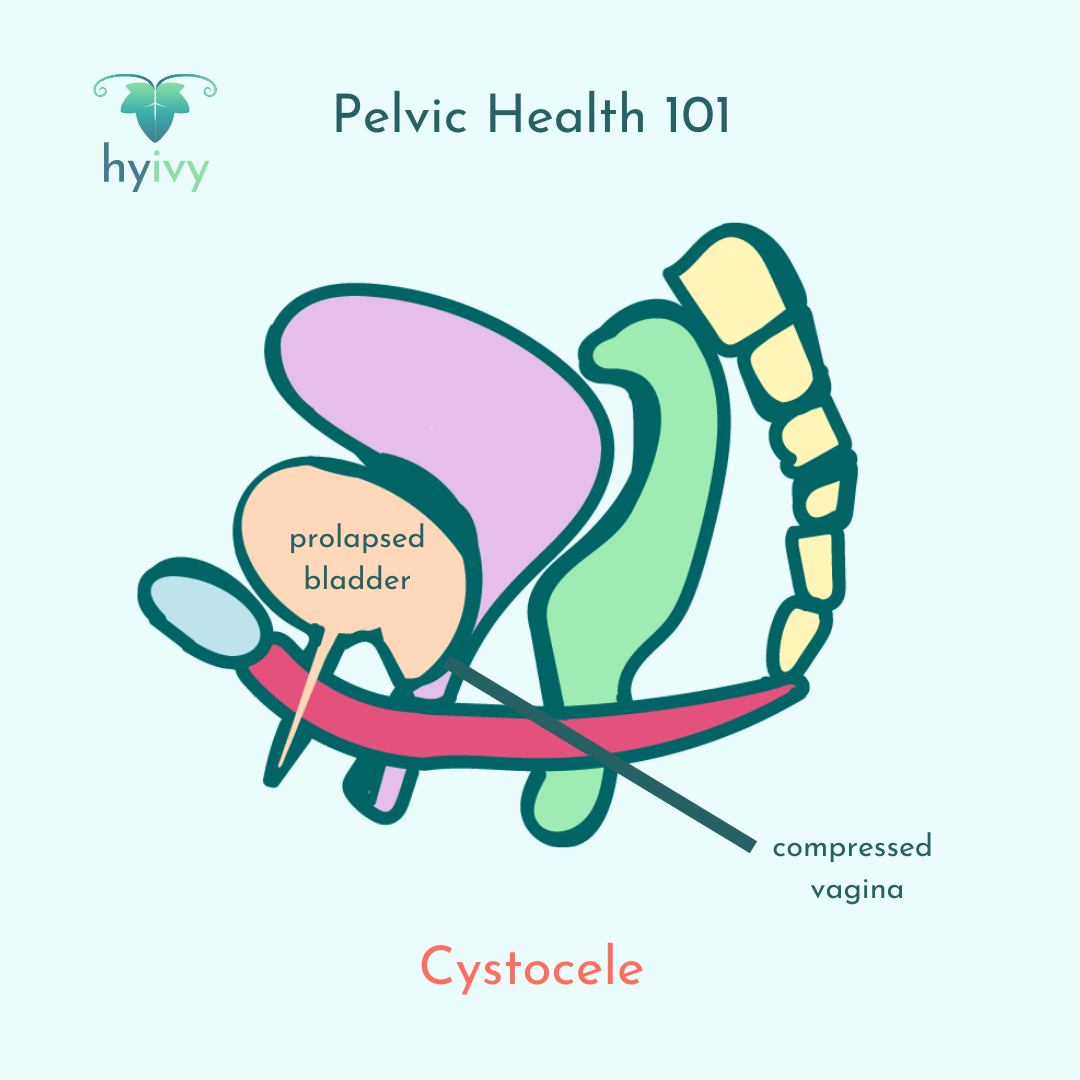
Cystocele is a condition in which the wall of supportive tissues between the vagina and bladder stretches or weakens. This weakening can cause the bladder to drop or bulge into the vagina. Cystocele is also sometimes called anterior vaginal prolapse, fallen or prolapsed bladder, or hernia of the bladder.
Dyspareunia is pain in the genitals or pelvic area occurring before, during, or after sexual intercourse.
Electrical stimulation is the use of low-grade electrical currents to stimulate muscles. A TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) machine delivers the electrical stimulation commonly used in pelvic floor therapy.
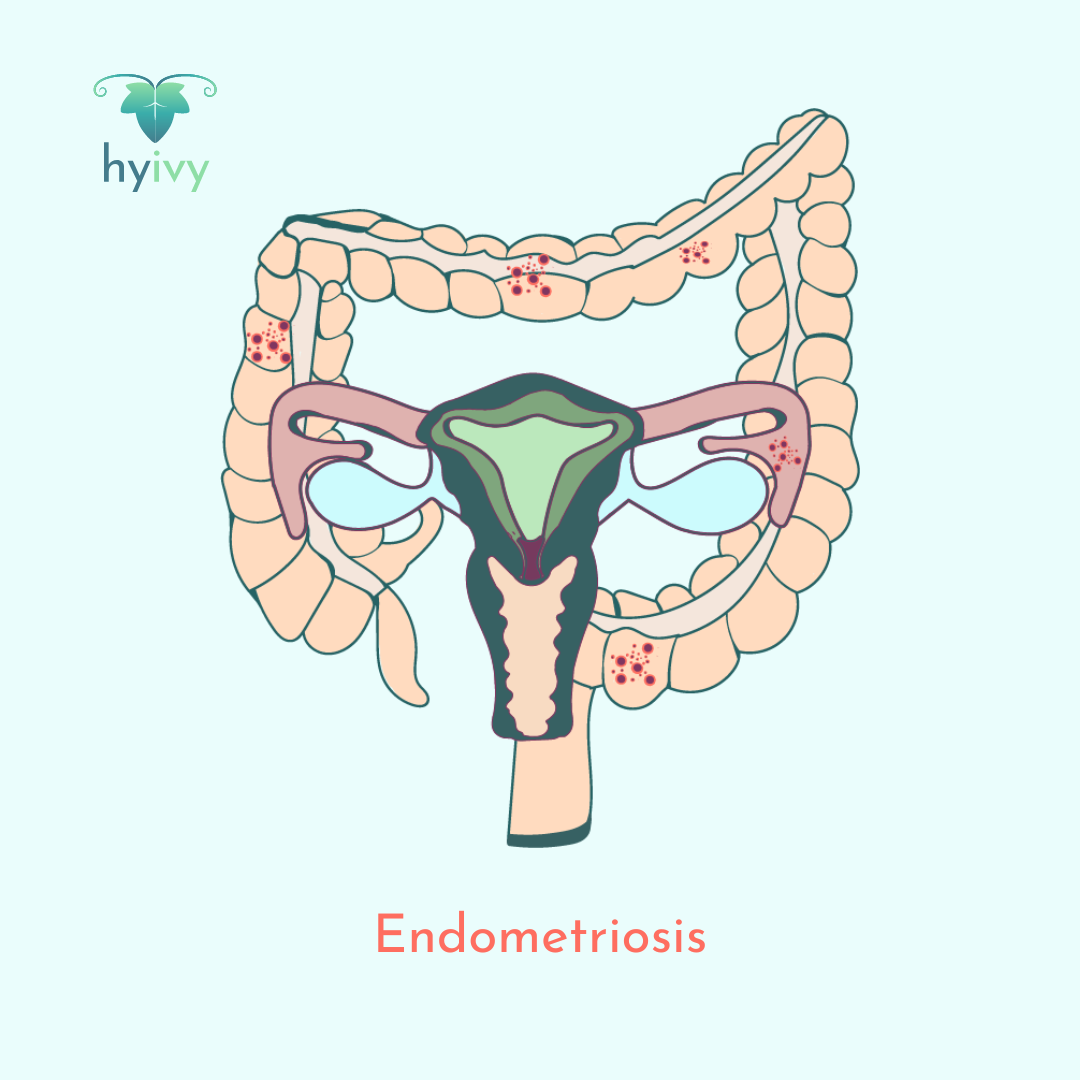
Endometriosis is a chronic condition in which tissue similar to endometrial tissue grows outside of the uterus (womb), causing scar tissue and/or adhesions in the pelvic region. Endometriosis can cause mild to severe pain during menstrual periods, sexual intercourse, bowel movements and/or urination, and can lead to symptoms such as chronic pelvic pain, abdominal bloating, heavy bleeding, nausea, fatigue, depression, and anxiety. Endometriosis can also lead to fertility complications.
Enterocele is a condition in which muscles, connective tissues, and ligaments in the pelvic region stretch or tear. This stretching causes the small intestine (small bowel) to drop into the lower pelvic cavity and push against the top of the vagina, creating a bulge.
Fecal incontinence (bowel incontinence) is the inability to control bowel movements. Urge fecal incontinence is the sensation of having to have a bowel movement without being able to make it to the toilet in time. Passive fecal incontinence is the passing of stool or mucus from the anus without awareness.
 Gender affirmation surgery is a general term encompassing procedures that help people transition to their self-identified gender. Some gender affirmation procedures include (but are not limited to): feminizing vaginoplasty, masculinizing phalloplasty/scrotoplasty, metoidioplasty (clitoral release/enlargement, urethral lengthening) masculinizing chest surgery (commonly known as top surgery), facial feminization procedures, reduction thyrochondroplasty (tracheal cartilage shave), and voice surgery.
Gender affirmation surgery is a general term encompassing procedures that help people transition to their self-identified gender. Some gender affirmation procedures include (but are not limited to): feminizing vaginoplasty, masculinizing phalloplasty/scrotoplasty, metoidioplasty (clitoral release/enlargement, urethral lengthening) masculinizing chest surgery (commonly known as top surgery), facial feminization procedures, reduction thyrochondroplasty (tracheal cartilage shave), and voice surgery.
Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM) is a relatively new term defined in 2014 that used to be known as vulvovaginal atrophy, atrophic vaginitis, or urogenital atrophy. GSM is a chronic condition that affects menopausal people who are experiencing a decrease in estrogen and progesterone. Common symptoms include: vaginal dryness, burning, itching, and irritation, decrease in vagina elasticity; loss of libido and impaired sexual function, pain with penetrative sex; painful urination; urinary urgency and frequency; and an increased risk of vaginal infections and UTIs.
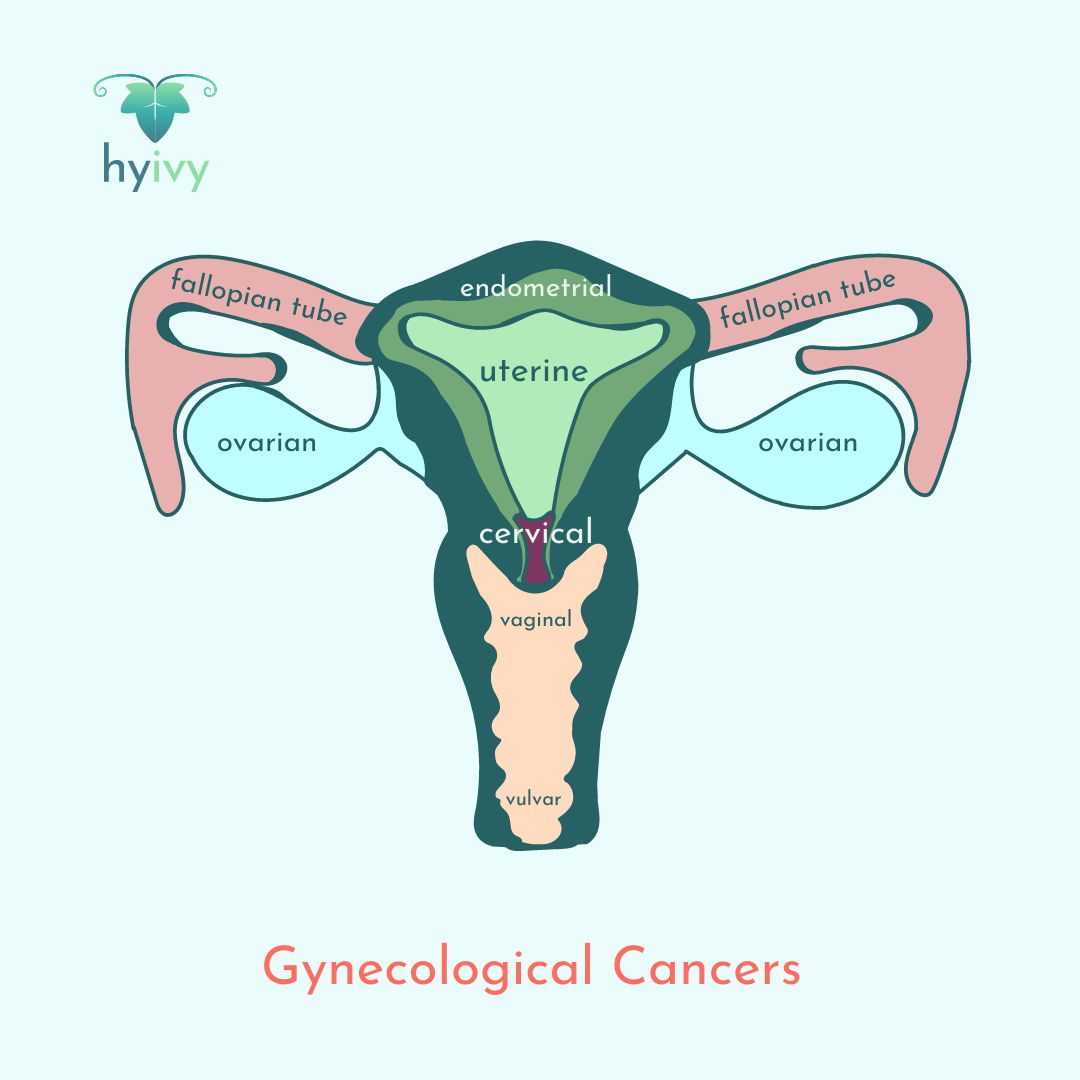 Gynecological cancers are cancers that start in the female reproductive system and are located in the pelvis. These include cervical, ovarian, endometrial/uterine, vaginal, vulvar, and fallopian tube cancers.
Gynecological cancers are cancers that start in the female reproductive system and are located in the pelvis. These include cervical, ovarian, endometrial/uterine, vaginal, vulvar, and fallopian tube cancers.
A gynecologist is a physician who has been specially trained in diagnosing and treating diseases related to the reproductive system of those assigned female at birth which includes: the vulva, uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, vagina, and breasts. You might see a gynecologist for menstrual issues, contraception, sexuality, menopause, or infertility issues. Many gynecologists also provide prenatal care, and some provide primary care.

Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a treatment used to relieve symptoms of menopause caused by falling levels of estrogen and progesterone. Unwanted symptoms of menopause include hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, urinary urgency, trouble sleeping, mood swings and mental health issues, dry skin, eyes, and mouth. HRT can be delivered by oral pills, skin patches, implants, gels, sprays, and oils. It’s important to speak with a certified healthcare professional to understand the risks and benefits.
HPV is an extremely common viral infection spread by intimate skin-to-skin contact. HPV consists of over 200 related viruses classified as low and high risk. Some HPV viruses cause no symptoms and can go away after time. Low-risk HPVs do not cause disease but may result in warts around your genitals, anus, mouth, or throat. High-risk HPVs are known to cause several types of cancer including cervical, oropharyngeal (mouth/throat), anal, penile, vaginal, and vulval cancer. HPV can infect anyone of any gender identity, sex, or sexual orientation.
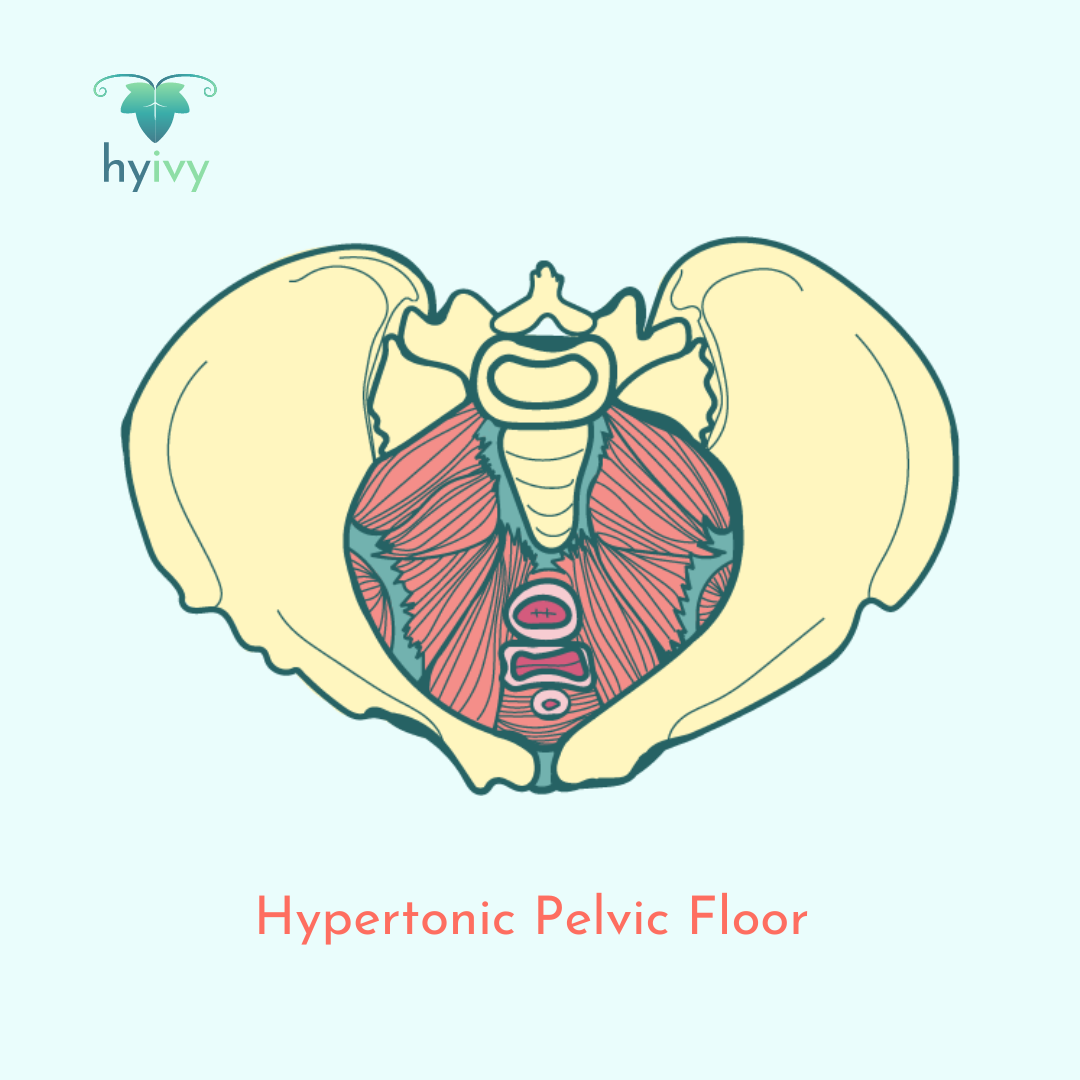 A hypertonic pelvic floor occurs when the pelvic floor muscles become too tight or tense and are unable to relax. A hypertonic pelvic floor can potentially cause: urinary frequency, urgency, or hesitancy; stopping and starting of urine streams; painful urination; incomplete emptying of the bladder; constipation or straining during bowel movements; pain during or after bowel movements; unexplained pain in the low back, pelvic region, hips, genital area, or rectum; pain during or after sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), sexual stimulation, or orgasms; and uncoordinated muscle contractions causing the pelvic floor muscles to spasm.
A hypertonic pelvic floor occurs when the pelvic floor muscles become too tight or tense and are unable to relax. A hypertonic pelvic floor can potentially cause: urinary frequency, urgency, or hesitancy; stopping and starting of urine streams; painful urination; incomplete emptying of the bladder; constipation or straining during bowel movements; pain during or after bowel movements; unexplained pain in the low back, pelvic region, hips, genital area, or rectum; pain during or after sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), sexual stimulation, or orgasms; and uncoordinated muscle contractions causing the pelvic floor muscles to spasm.
A hypotonic pelvic floor occurs when the muscles in the pelvic floor become too weak to function as needed. A hypotonic pelvic floor can potentially cause: urinary or fecal incontinence, pain or pressure in the pelvic area, pelvic organ prolapse, or decreased sensation during sexual intercourse.
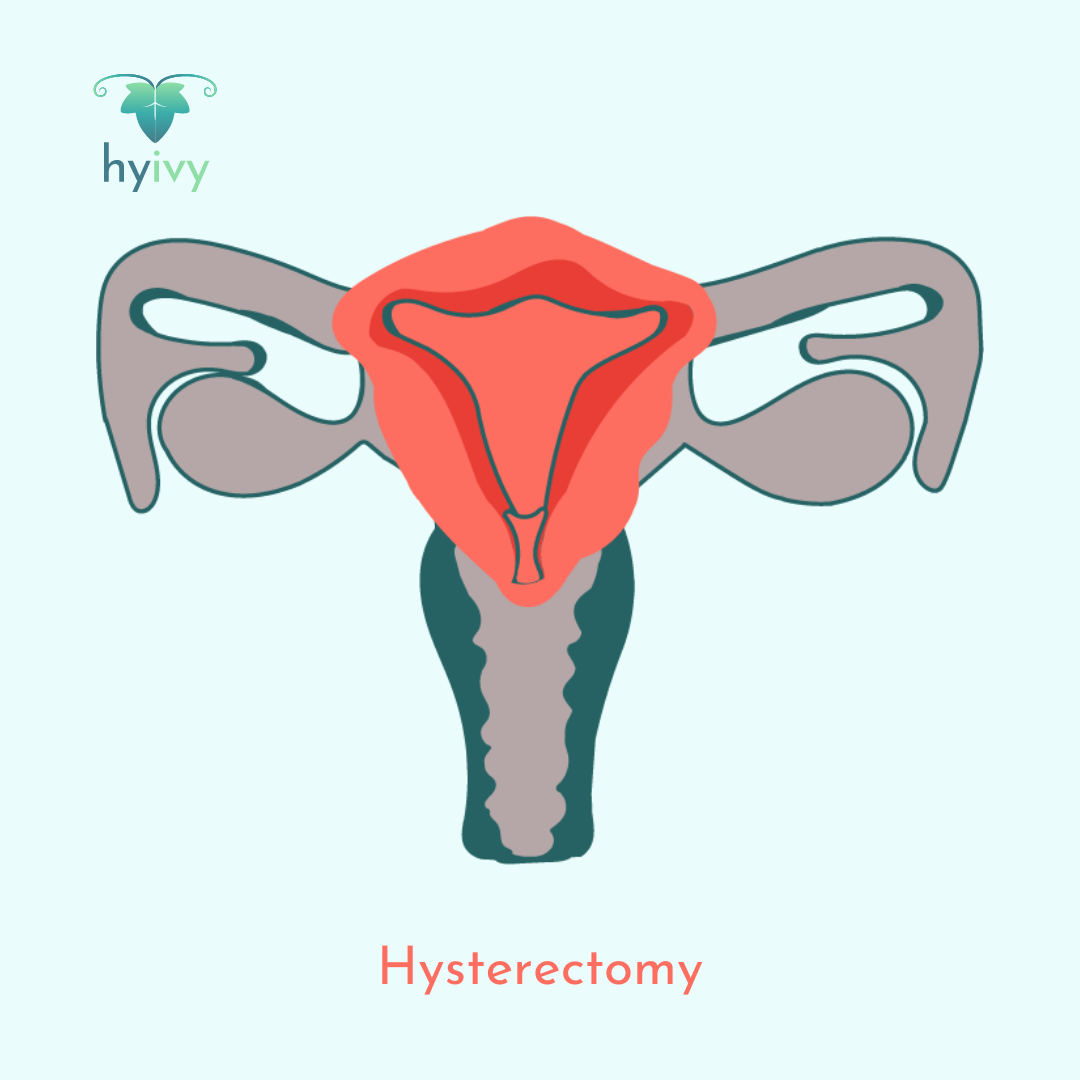 A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus (womb). A partial hysterectomy removes just the uterus, leaving the cervix intact. A total hysterectomy removes the uterus and the cervix. A hysterectomy that includes the removal of fallopian tubes and one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) ovaries is called a total hysterectomy with salpingo-oophorectomy.
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the uterus (womb). A partial hysterectomy removes just the uterus, leaving the cervix intact. A total hysterectomy removes the uterus and the cervix. A hysterectomy that includes the removal of fallopian tubes and one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) ovaries is called a total hysterectomy with salpingo-oophorectomy.
People of all gender orientations and sex can experience infertility. Some common causes of infertility are hormonal and genetic disorders, PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome), diminished ovarian reserve, hypothalamus and pituitary glands issues, menopause, and disruption of testicular or ejaculatory function. 1 in 6 people worldwide will experience some form of infertility.
Inflammation is the immune system’s response to a variety of factors, including pathogens (bacteria, viruses, or other organisms), damage from foreign objects, or exposure to chemicals or radiation. Symptoms of inflammation can include: pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function in the affected area.
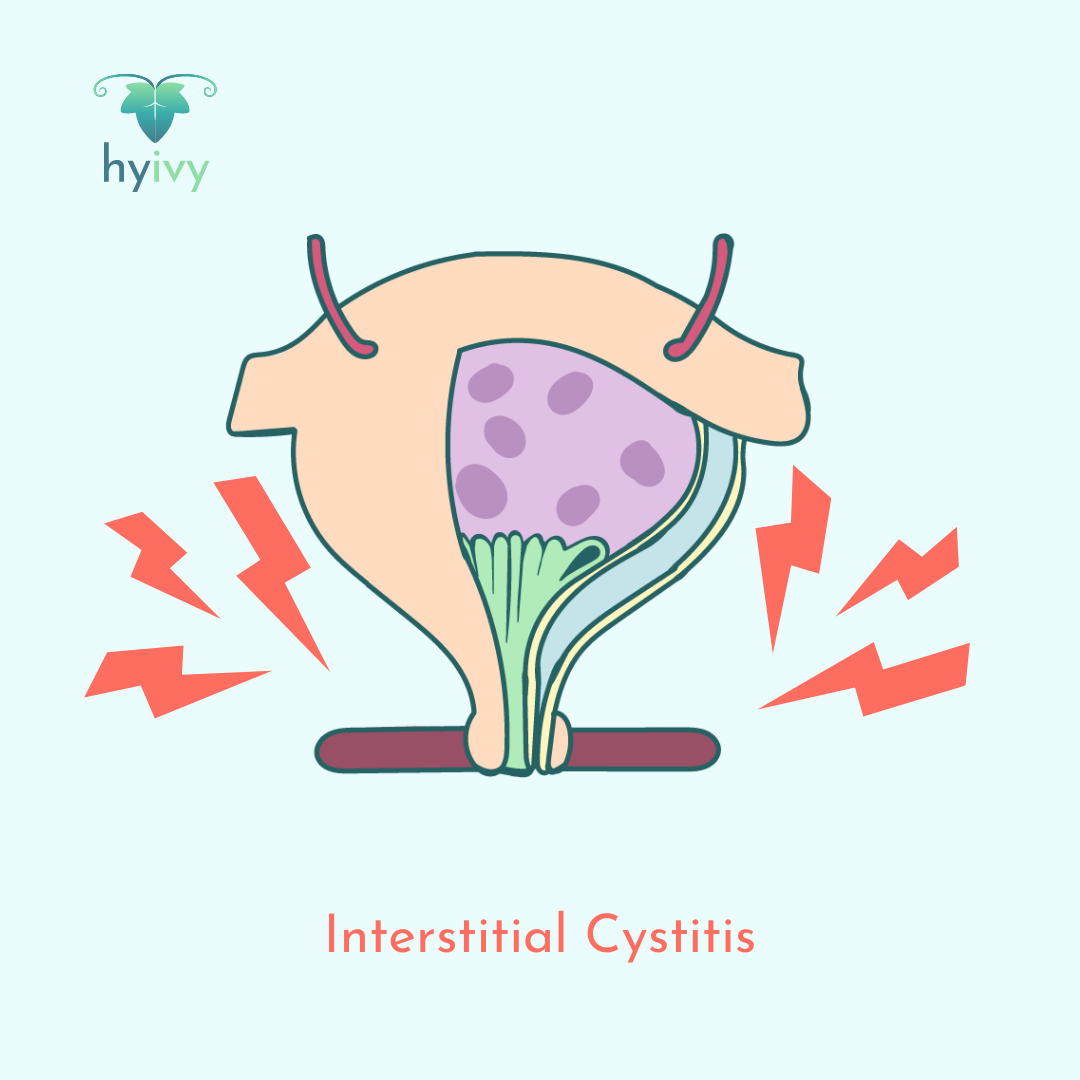 Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome) is a chronic condition identified by lower urinary tract symptoms experienced for more than six weeks without infection or other causes. Symptoms of interstitial cystitis can include: bladder pain, pressure, urinary frequency and urgency, and mild to severe pelvic pain.
Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome) is a chronic condition identified by lower urinary tract symptoms experienced for more than six weeks without infection or other causes. Symptoms of interstitial cystitis can include: bladder pain, pressure, urinary frequency and urgency, and mild to severe pelvic pain.
Kegel exercises aim to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles in order to support the uterus, bladder, small intestine, and rectum. Kegel exercises are typically performed by lifting, holding, and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles. Kegel exercisers (kegel devices) include insertable trainers, weights, and biofeedback devices.
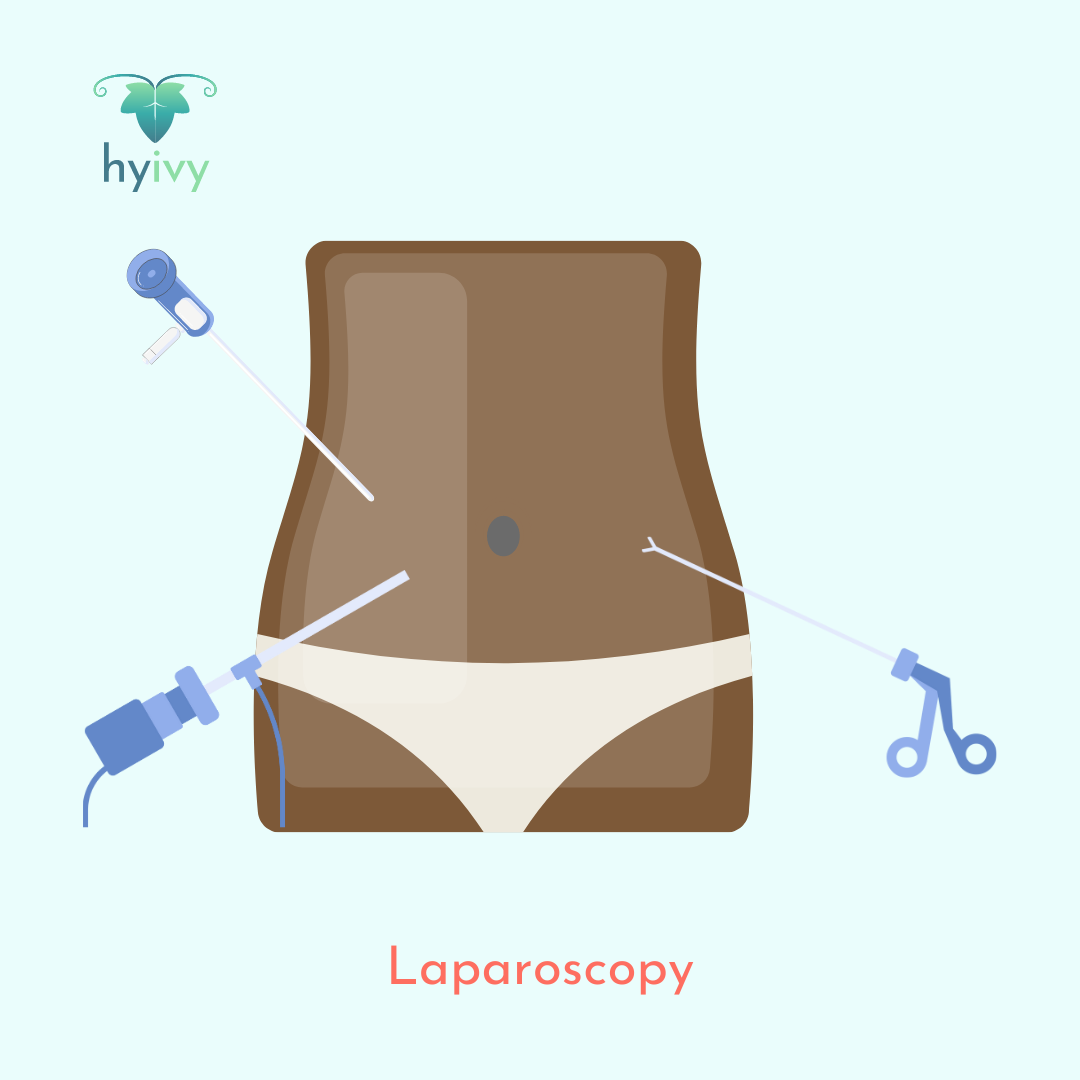 Laparoscopy (keyhole surgery or minimally invasive surgery) is a type of surgical procedure that allows access to the inside of the abdomen (belly) and pelvis without having to make larger incisions or cuts in the skin. Laparoscopy uses a small instrument called a laparoscope, a small tube equipped with a light source and camera.
Laparoscopy (keyhole surgery or minimally invasive surgery) is a type of surgical procedure that allows access to the inside of the abdomen (belly) and pelvis without having to make larger incisions or cuts in the skin. Laparoscopy uses a small instrument called a laparoscope, a small tube equipped with a light source and camera.
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that can appear anywhere on the body but is commonly found around the genitals and anus. Symptoms can include: white lesions or plaques, pain with urination, mild to severe itching, pain with sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), and blistering.
 Loss of libido is defined as inhibited sexual desire or inability to sustain sexual arousal during sexual activities. There is a wide range of causes for loss of libido, including underlying medical, personal, or lifestyle issues.
Loss of libido is defined as inhibited sexual desire or inability to sustain sexual arousal during sexual activities. There is a wide range of causes for loss of libido, including underlying medical, personal, or lifestyle issues.
 Menopause marks the end of permanent menstruation and fertility. Menopause can be caused by the natural biological process (often beginning at age 40-50), a surgery to remove the ovaries (oophorectomy), radiation or chemotherapy, and primary ovarian insufficiency. Menopause has over 35 physical and emotional symptoms including: hot flashes; irregular, heavy, or missed periods; sleeping issues; bladder issues such as UTIs or urinary incontinence; night sweats; vaginal dryness; painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia); decrease in fertility; changes to libido; loss of bone density; changing cholesterol levels; mood swings; weight gain; and thinning hair.
Menopause marks the end of permanent menstruation and fertility. Menopause can be caused by the natural biological process (often beginning at age 40-50), a surgery to remove the ovaries (oophorectomy), radiation or chemotherapy, and primary ovarian insufficiency. Menopause has over 35 physical and emotional symptoms including: hot flashes; irregular, heavy, or missed periods; sleeping issues; bladder issues such as UTIs or urinary incontinence; night sweats; vaginal dryness; painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia); decrease in fertility; changes to libido; loss of bone density; changing cholesterol levels; mood swings; weight gain; and thinning hair.
Menstruation (the period) starts when an egg from the previous cycle is not fertilized and the thickened lining of the uterus (the endometrium) exits the body through the vagina. Bleeding typically lasts for 3-8 days. The length of time from the first day of one period to the first day of the next period ranges from 21-35 days (a cycle).
An OB/GYN is a physician who specializes in both obstetrics and gynecology. Obstetrics includes the care for pregnancy, labor, childbirth and the postpartum period. Gynecology includes the care of the reproductive system of those assigned female at birth which includes: the vulva, uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix, vagina, and breasts. You might see a gynecologist for menstrual issues, contraception, sexuality, menopause, or infertility issues.
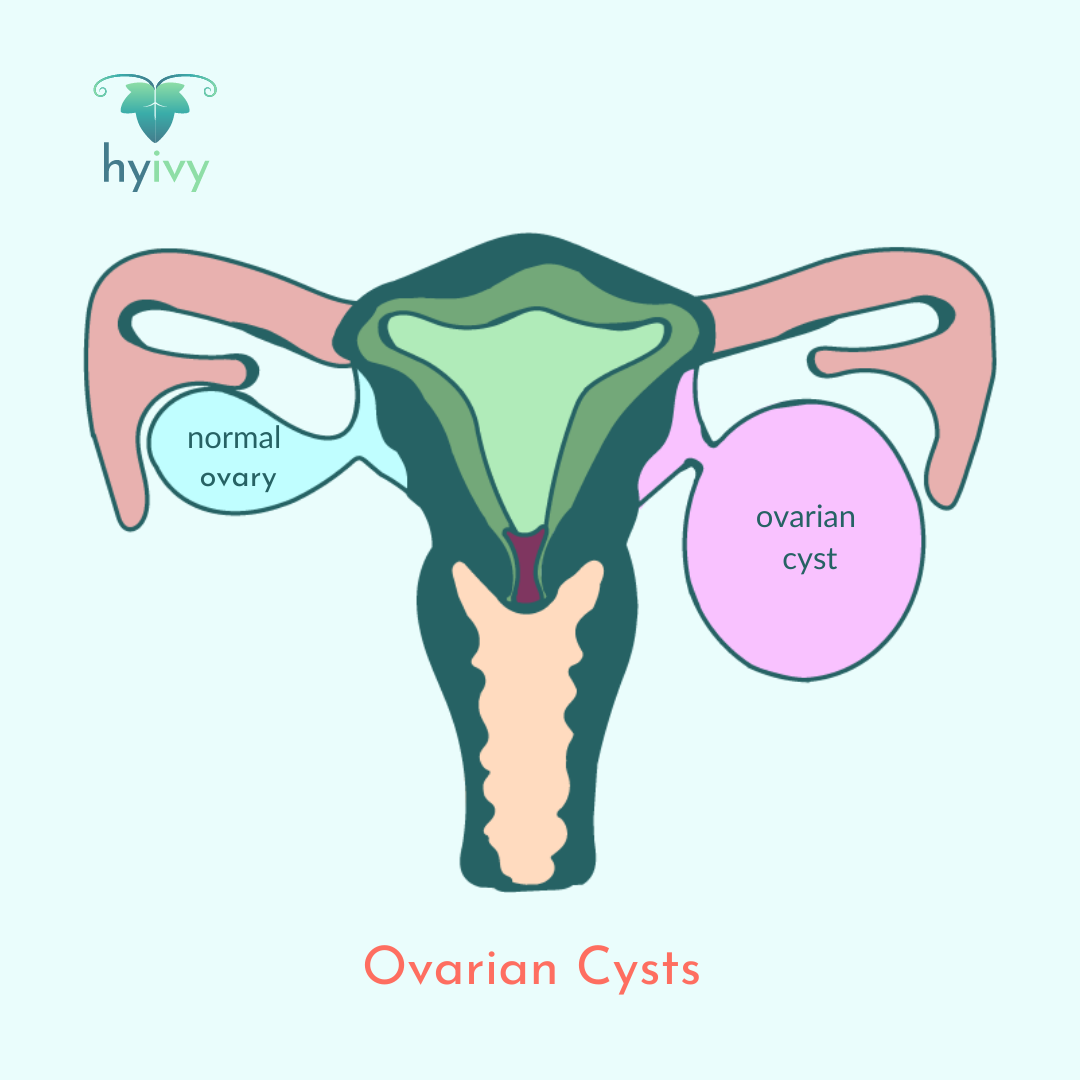 Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form on the ovaries (some cysts may have tissue inside of them). Ovarian cysts are quite common. They are typically 2-3 centimeters in size. They are not typically symptomatic and disappear without treatment. Ovarian cysts can cause problems if they rupture, are very large, or block the blood supply to the ovaries, which can cause: pelvic pain, pain with sexual intercourse, difficulty emptying bowels, frequent need to urinate, heavy bleeding during periods, irregular periods, bloating or swollen abdomen, feeling of fullness after eating smaller portions, and difficulty getting pregnant.
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form on the ovaries (some cysts may have tissue inside of them). Ovarian cysts are quite common. They are typically 2-3 centimeters in size. They are not typically symptomatic and disappear without treatment. Ovarian cysts can cause problems if they rupture, are very large, or block the blood supply to the ovaries, which can cause: pelvic pain, pain with sexual intercourse, difficulty emptying bowels, frequent need to urinate, heavy bleeding during periods, irregular periods, bloating or swollen abdomen, feeling of fullness after eating smaller portions, and difficulty getting pregnant.
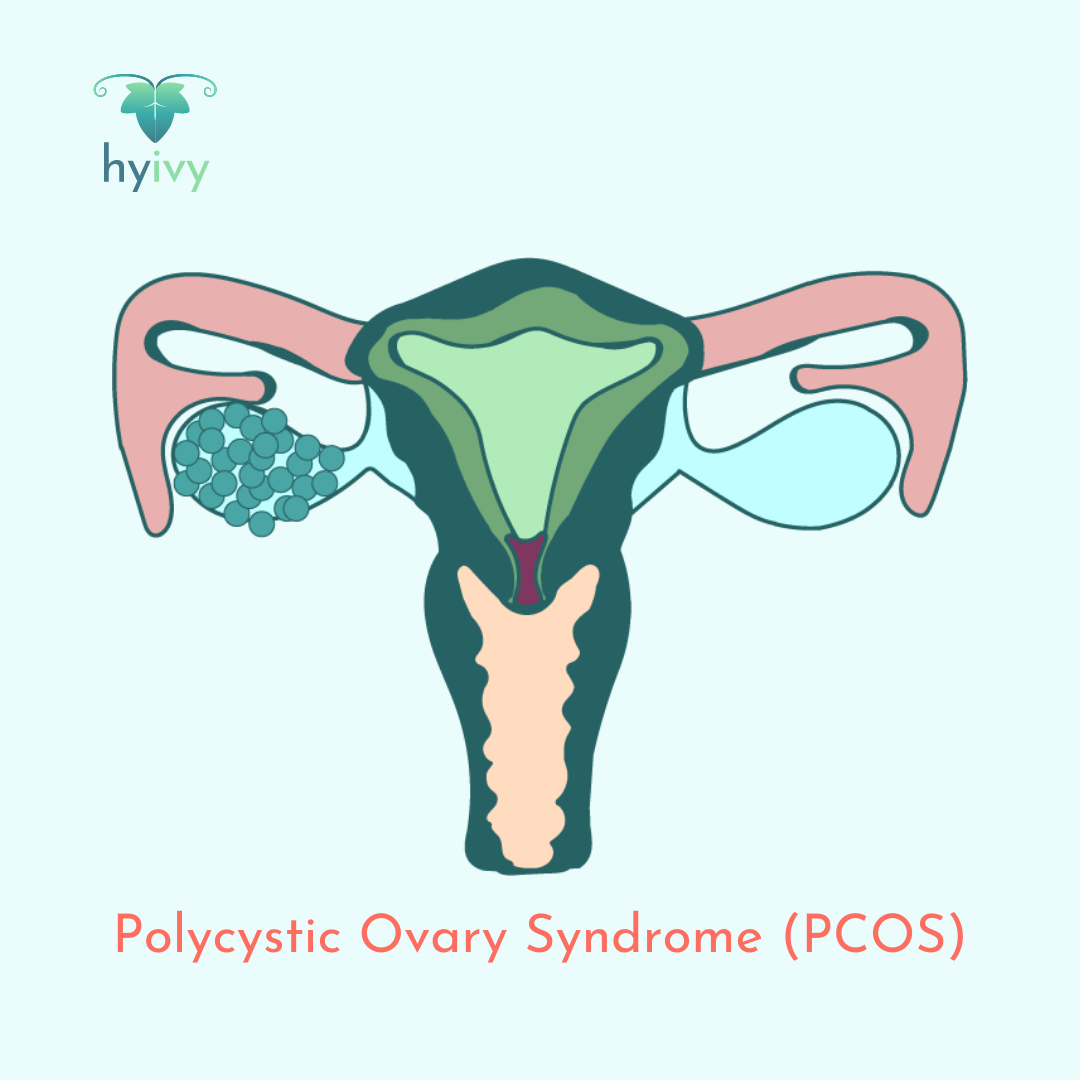 Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which the ovaries produce abnormal amounts of androgens (a group of hormones that includes testosterone). Signs and symptoms can include: irregular, light, or missed periods; difficulty getting pregnant; excessive hair growth (hirsutism) on the face, chest, back, or buttocks; weight gain; thinning hair or hair loss on the head; and oily skin or acne. PCOS has also been associated with the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol levels.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which the ovaries produce abnormal amounts of androgens (a group of hormones that includes testosterone). Signs and symptoms can include: irregular, light, or missed periods; difficulty getting pregnant; excessive hair growth (hirsutism) on the face, chest, back, or buttocks; weight gain; thinning hair or hair loss on the head; and oily skin or acne. PCOS has also been associated with the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol levels.
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles that stretch from the tailbone (coccyx) to the pubic bone at the front and between the sitz bones from one side to the other. The pelvic floor muscles act as a hammock, providing the main support for the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor also serves multiple functions, such as urinary continence, defecation, and fecal continence.
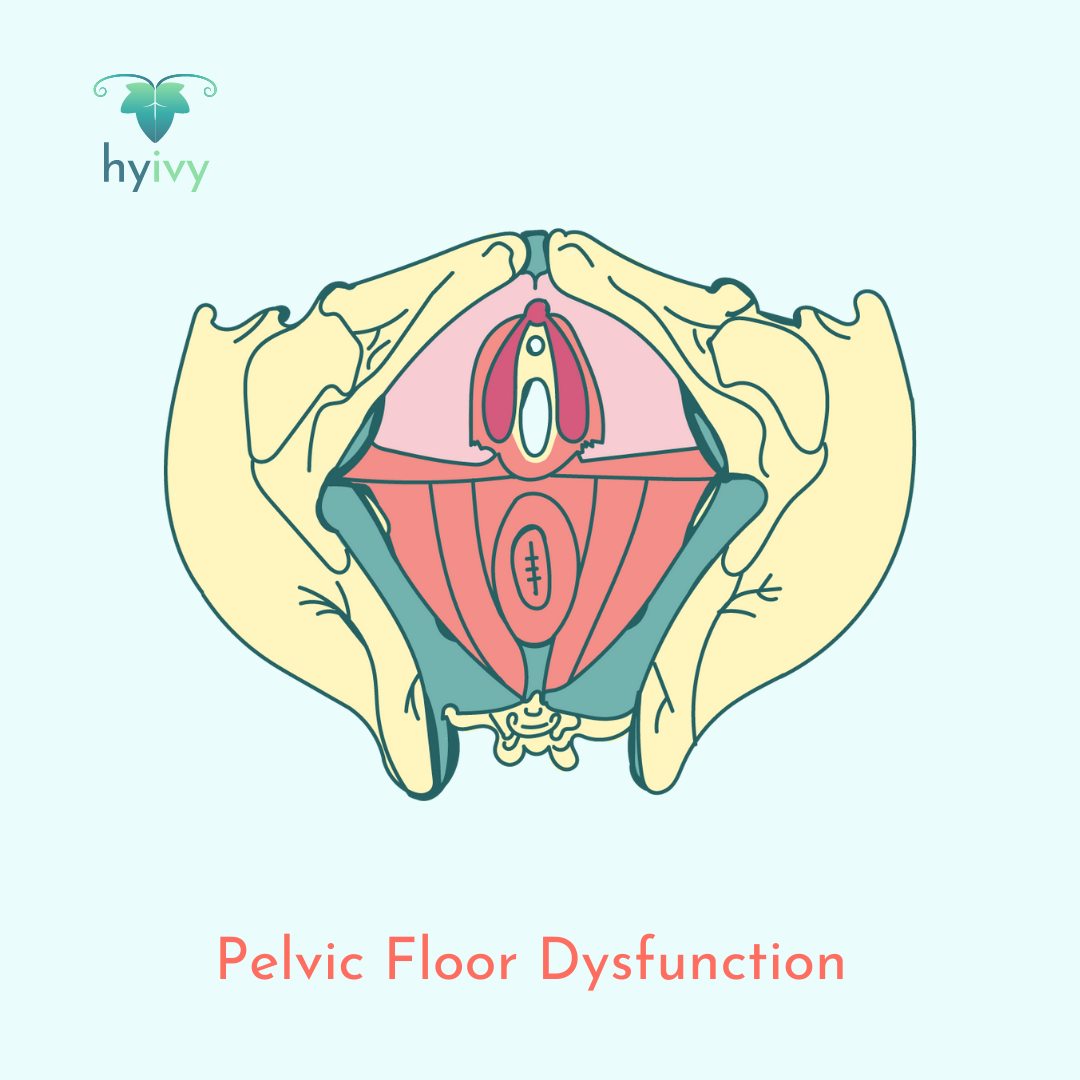 Pelvic floor dysfunction is the inability to control the muscles of the pelvic floor. Symptoms can include: urge to urinate or painful urination; constipation or straining during a bowel movement; lower back pain; pain in the pelvic region, genitals, or rectum; discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia); difficulty keeping an erection; pressure on the pelvic region or rectum; and muscle spasms in the pelvis.
Pelvic floor dysfunction is the inability to control the muscles of the pelvic floor. Symptoms can include: urge to urinate or painful urination; constipation or straining during a bowel movement; lower back pain; pain in the pelvic region, genitals, or rectum; discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia); difficulty keeping an erection; pressure on the pelvic region or rectum; and muscle spasms in the pelvis.
Pelvic floor physiotherapists (or PFPTs) work to help you rehabilitate your pelvic floor muscles. They are specially trained to conduct internal and external assessments and treatments for your pelvic floor. Symptoms that might cause you to seek out the pelvic floor physiotherapy are pain in the (pelvis) pelvic, lower back, or genital region, urinary incontinence or frequency, pelvic organ prolapse (POP), pain with sex (dyspareunia) or when trying to insert a tampon, or difficulty emptying the bladder or bowels.
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is when one or more organs in the pelvis drop into or press against the vagina. Types of POP include: prolapse of the bladder (cystocele), the rectum (rectocele), the urethra (urethrocele), the uterus (uterine prolapse), the top of the vagina after a hysterectomy (vaginal vault prolapse), and the intestines (enterocele).
Perimenopause is the transition phase around and leading up to menopause. Perimenopause can last for 4-10 years and often begins in a person’s 40s or 50s. Perimenopause ends one year after the final menstrual period. Symptoms of perimenopause can include: hot flashes; irregular, heavy, or missed periods; sleeping issues; bladder issues such as UTIs or urinary incontinence; night sweats; vaginal dryness; painful sexual intercourse; a decrease in fertility; changes to libido; loss of bone density; changing cholesterol levels; mood swings; weight gain; and thinning hair.
Persistent genital arousal disorder (PGAD) or persistent sexual arousal syndrome (PSAS) is an arousal disorder in which females experience spontaneous genital arousal triggered by sexual or nonsexual stimuli. Sexual arousal experienced in PGAD is unresolved by orgasms and often causes distress.
 Personal lubricant (lube) is a liquid or gel used to reduce friction or irritation during sexual activity (penetrative sex, anal sex, masturbation, and sex toy play). Types of lubes include water-based, silicone-based, oil-based, and hybrids.
Personal lubricant (lube) is a liquid or gel used to reduce friction or irritation during sexual activity (penetrative sex, anal sex, masturbation, and sex toy play). Types of lubes include water-based, silicone-based, oil-based, and hybrids.
A pessary is a prosthetic device that is inserted into the vagina. It is typically used to support organs that have dropped down into or are pressing against the vagina (like with cystocele and rectocele), or to help with stress urinary incontinence.
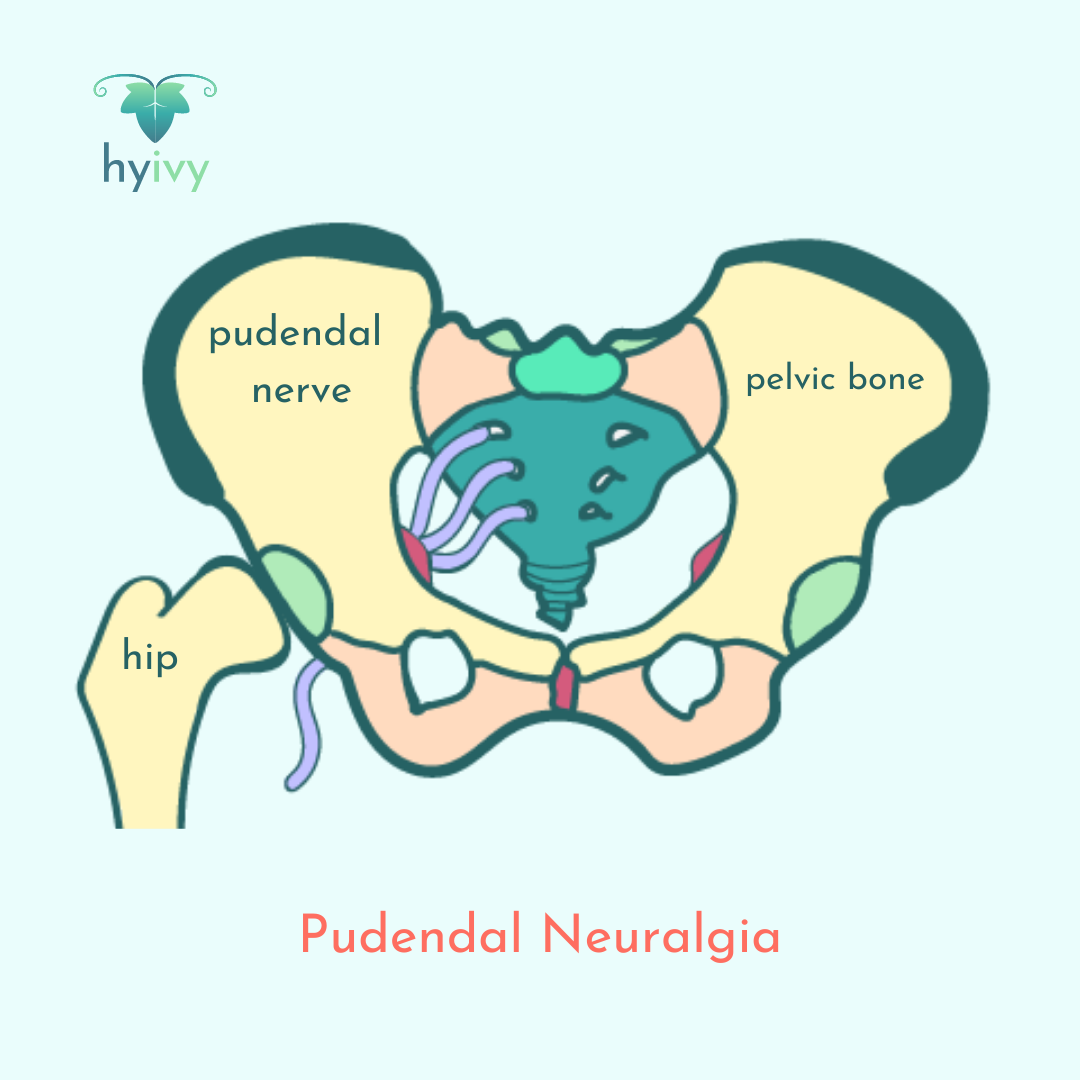 Pudendal neuralgia is chronic pelvic pain originating from damage to or irritation of the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the pelvis made up of sensory, motor, and autonomic fibers that runs through the lower buttocks, perineum (area between the buttocks and genitals), area around the anus and the rectum, vulva, labia, clitoris, and scrotum.
Pudendal neuralgia is chronic pelvic pain originating from damage to or irritation of the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the pelvis made up of sensory, motor, and autonomic fibers that runs through the lower buttocks, perineum (area between the buttocks and genitals), area around the anus and the rectum, vulva, labia, clitoris, and scrotum.
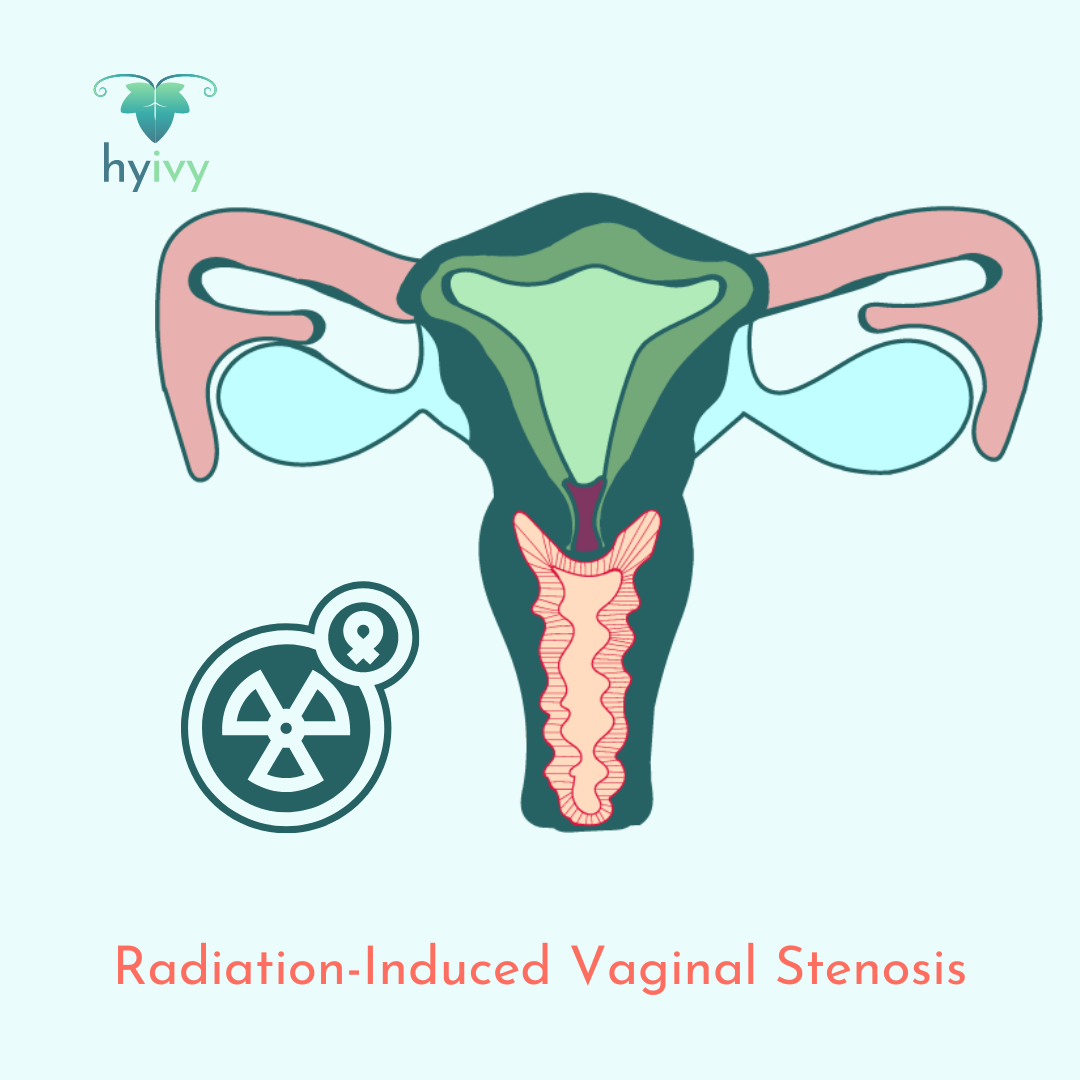 Radiation-induced vaginal stenosis is vaginal stenosis caused by radiation therapy for cancer treatment. Vaginal stenosis is defined as the narrowing and shortening of the vagina caused by scar tissue. Vaginal stenosis can cause painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), painful pelvic exams, and vaginal dryness.
Radiation-induced vaginal stenosis is vaginal stenosis caused by radiation therapy for cancer treatment. Vaginal stenosis is defined as the narrowing and shortening of the vagina caused by scar tissue. Vaginal stenosis can cause painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), painful pelvic exams, and vaginal dryness.
Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) is a cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. There are various long- and short-term side effects from radiation therapy which vary from person to person and depend on your health history and your course of treatment.
Rectocele (posterior vaginal wall prolapse) is a condition in which the wall between the rectum and the vagina weakens, resulting in the bulging of the rectum into the vaginal wall. This can cause a feeling of “fullness” in the bowels even though they have been recently emptied, discomfort from the bulging in the vagina, difficulty with bowel movements, and the inability to control bowel movements.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) are caused by organisms such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites passed from one person to another during sexual intercourse, oral sex, or other intimate contact. STIs can be transmitted through unprotected oral, vaginal, and anal sex, or skin-to-skin contact.
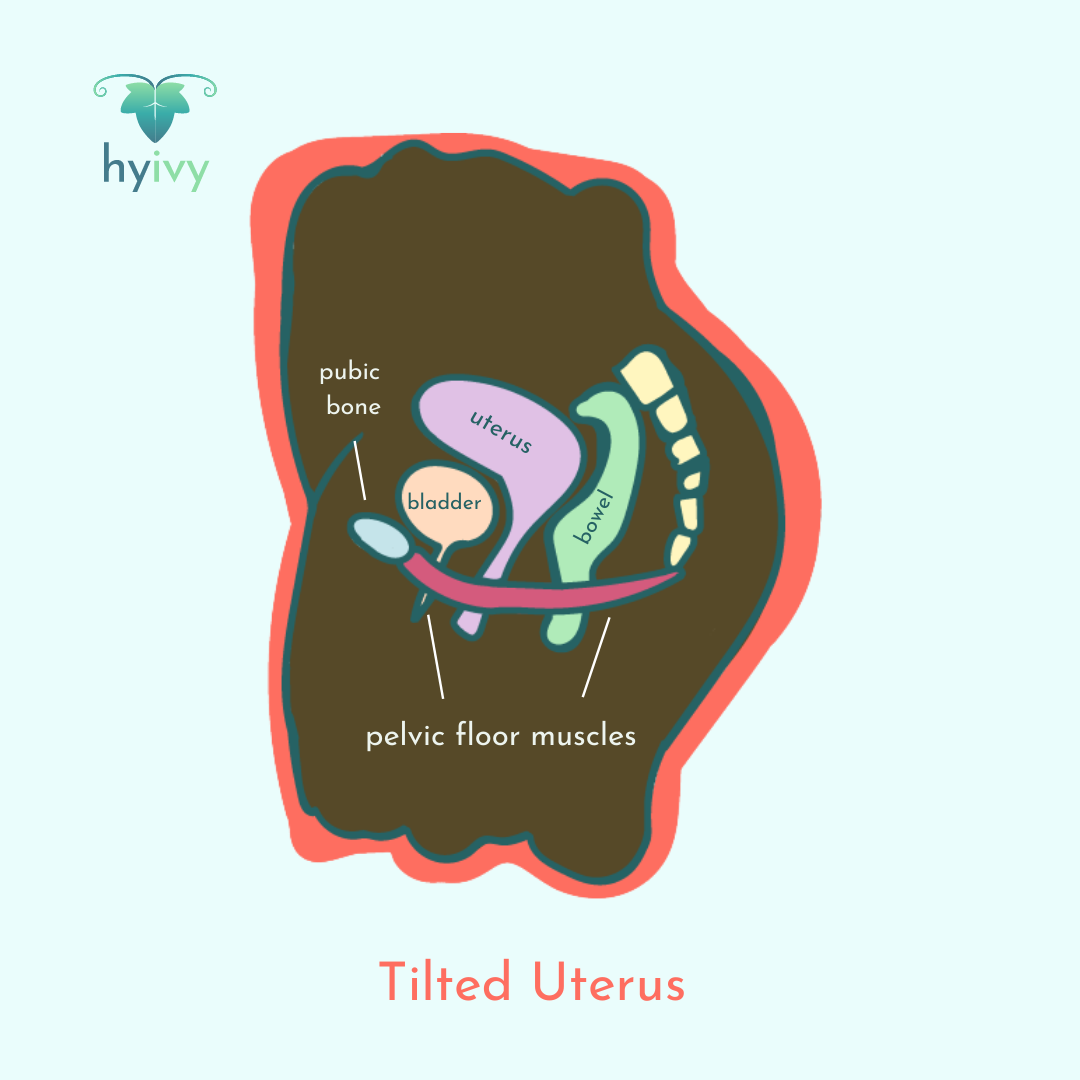 Tilted uterus (retroverted, tipped, backward, retroflexed, or uterine retro displacement) is a uterus that is tipped backwards towards the rectum as opposed to tipping forward towards the abdomen (belly). Some people with tilted uterus may experience pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), menstruation, and inserting tampons; increased urinary frequency; urinary tract infections (UTIs); urinary incontinence; and protrusion of the lower abdomen.
Tilted uterus (retroverted, tipped, backward, retroflexed, or uterine retro displacement) is a uterus that is tipped backwards towards the rectum as opposed to tipping forward towards the abdomen (belly). Some people with tilted uterus may experience pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), menstruation, and inserting tampons; increased urinary frequency; urinary tract infections (UTIs); urinary incontinence; and protrusion of the lower abdomen.
Urethrocele (urethral prolapse) is a condition in which the tube that carries urine from the bladder (the urethra) is not supported by the muscles or tissue around it, causing it to curve or widen. Urethrocele can cause urinary incontinence or leakage, especially with coughing, jumping, or laughing.
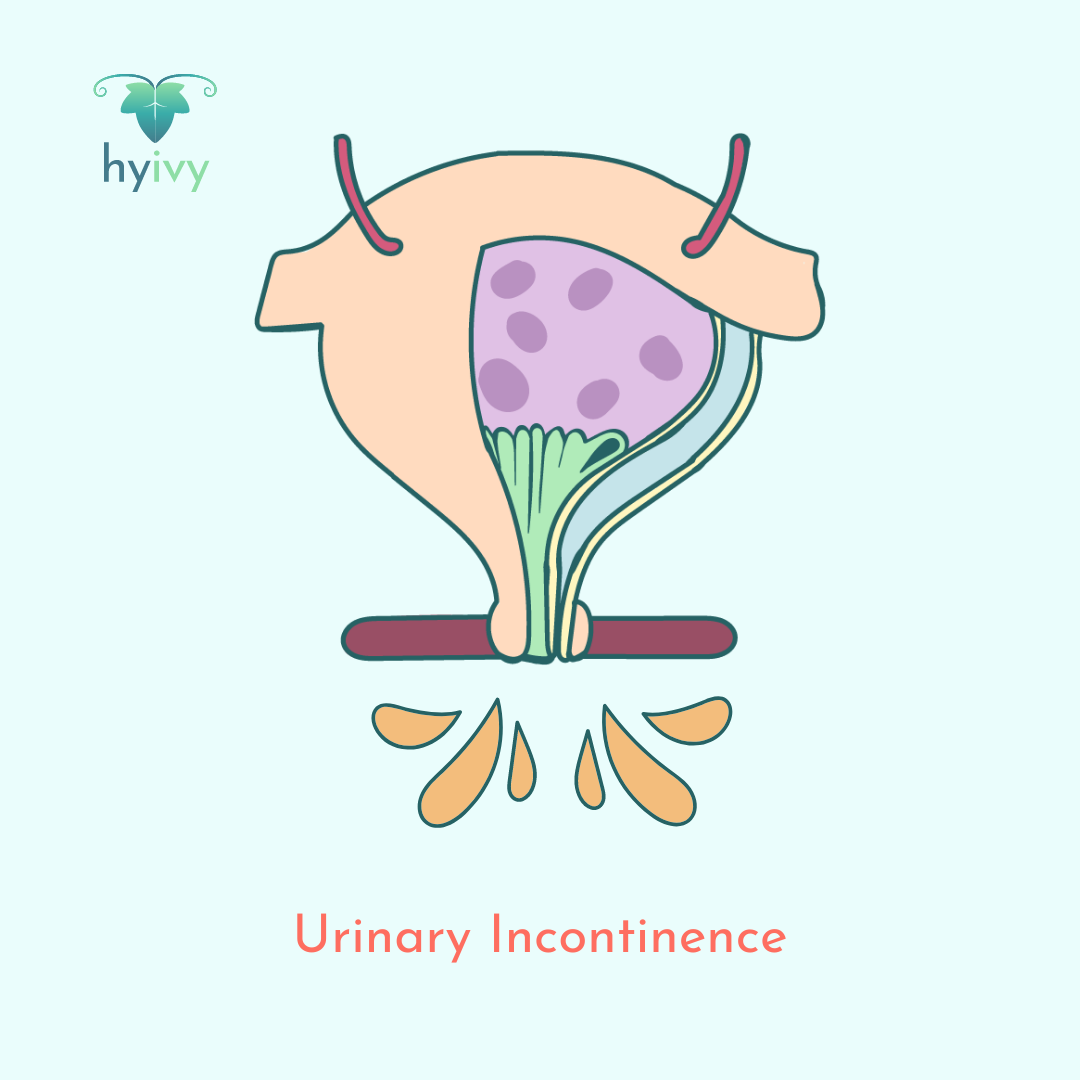 Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine and can be a symptom of many conditions. Urinary incontinence includes: stress urinary incontinence (SUI), in which stretched and weak pelvic floor muscles allow urine to escape (typically caused by physical activity, sneezing, coughing or laughing); urgency incontinence or overactive bladder (OAB), which feels like a sudden urge to urinate; mixed urinary incontinence, in which both SUI and OAB are experienced; and overflow incontinence, in which the body makes more urine than the bladder can hold, causing it to leak.
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine and can be a symptom of many conditions. Urinary incontinence includes: stress urinary incontinence (SUI), in which stretched and weak pelvic floor muscles allow urine to escape (typically caused by physical activity, sneezing, coughing or laughing); urgency incontinence or overactive bladder (OAB), which feels like a sudden urge to urinate; mixed urinary incontinence, in which both SUI and OAB are experienced; and overflow incontinence, in which the body makes more urine than the bladder can hold, causing it to leak.
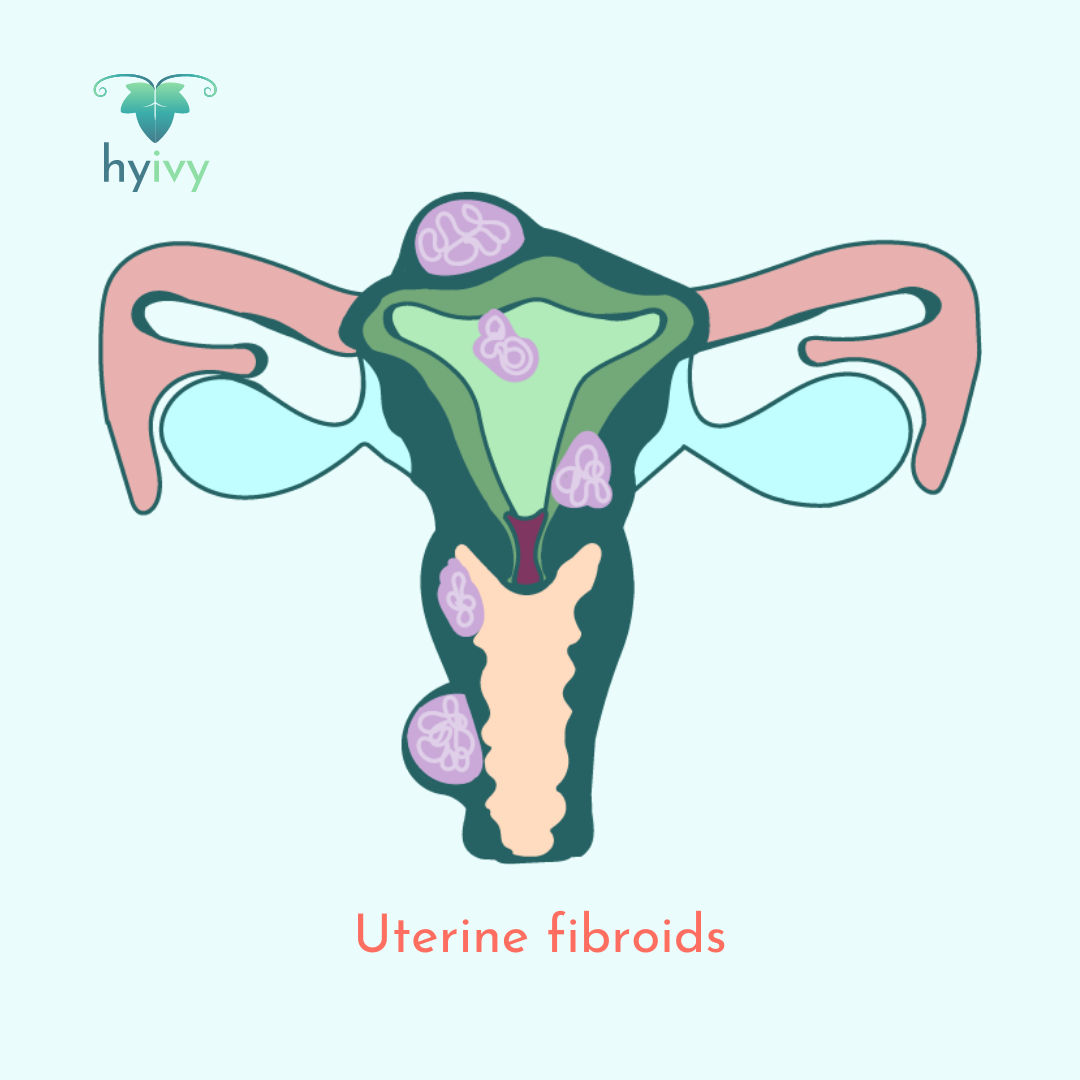 Uterine fibroids (fibroid tumors, leiomyomas, or myomas) are noncancerous (benign) muscular tumors that grow in the wall of the uterus (womb). Symptoms can include long and heavy periods, cramping, a feeling of fullness or pressure on the abdomen (belly), low back pain, pain with sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), and the frequent urge to urinate.
Uterine fibroids (fibroid tumors, leiomyomas, or myomas) are noncancerous (benign) muscular tumors that grow in the wall of the uterus (womb). Symptoms can include long and heavy periods, cramping, a feeling of fullness or pressure on the abdomen (belly), low back pain, pain with sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), and the frequent urge to urinate.
Uterine prolapse occurs when the muscles and tissues in the pelvis weaken, causing the uterus (womb) to hang or bulge down into the vagina. Symptoms can include: a feeling of pressure or heaviness in the pelvis, pain in the pelvis, pain in the abdomen or lower back, pain with sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), uterine tissue falling through the opening of the vagina, frequent bladder infections, unusual discharge from the vagina, chronic constipation, and urinary incontinence.
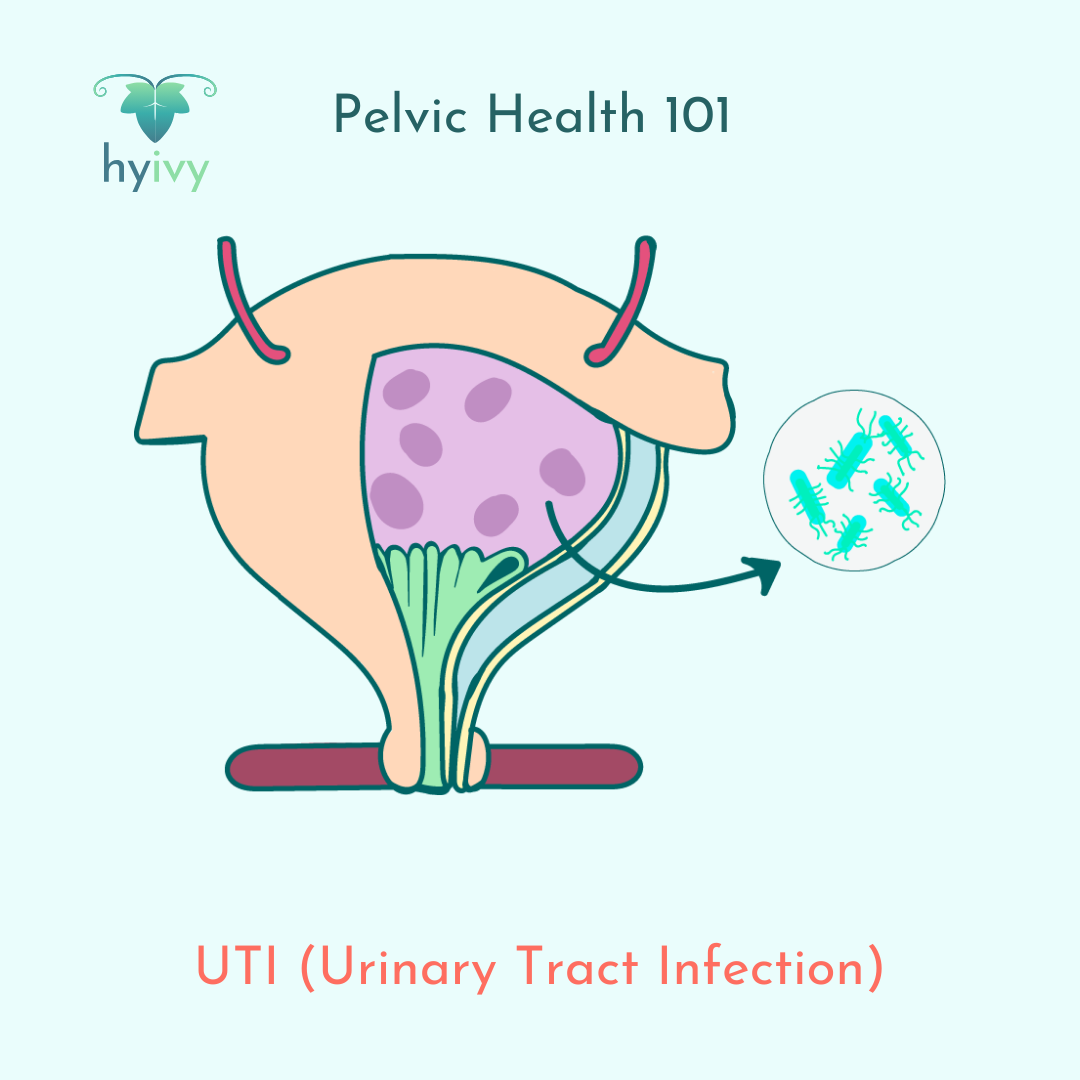
UTIs are common infections that occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to spread into the bladder. Common symptoms include: pain or a burning sensation when you urinate, a strong urge to urinate that doesn’t go away even after you’ve emptied your bladder, frequent urination where you can only pass small amounts of urine, cloudy, bloody, or bright pink urine, strong smelling urine, pelvic pain, pressure in your lower back or pelvis, and some UTIs may cause mental confusion or a temporary state of delirium.
 Vaginal atrophy (atrophic vaginitis) is the thinning, drying, and inflammation of the vaginal walls. Vaginal atrophy commonly occurs after menopause, when the body produces less estrogen. Symptoms can include: painful sexual intercourse, increase in urinary frequency, or urge urinary incontinence.
Vaginal atrophy (atrophic vaginitis) is the thinning, drying, and inflammation of the vaginal walls. Vaginal atrophy commonly occurs after menopause, when the body produces less estrogen. Symptoms can include: painful sexual intercourse, increase in urinary frequency, or urge urinary incontinence.
 Vaginal dilators (inserts) are plastic or silicone rods or cylinders with a rounded tip. They are meant to open (dilate) and stretch the tissues of the vagina.
Vaginal dilators (inserts) are plastic or silicone rods or cylinders with a rounded tip. They are meant to open (dilate) and stretch the tissues of the vagina.
 Vaginal discharge is a fluid or mucus that comes out of the vagina and keeps the vagina clean and moist, preventing infection. Typical vaginal discharge is white or clear (can be brown or bloody around the menstrual cycle), thick, sticky, slippery, wet, and has a neutral smell. Abnormal vaginal discharge is yellow or green colored, is thick and white with the texture of cottage cheese, and can have a strong or unpleasant smell. Abnormal vaginal discharge can also be accompanied by pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, and blisters or sores.
Vaginal discharge is a fluid or mucus that comes out of the vagina and keeps the vagina clean and moist, preventing infection. Typical vaginal discharge is white or clear (can be brown or bloody around the menstrual cycle), thick, sticky, slippery, wet, and has a neutral smell. Abnormal vaginal discharge is yellow or green colored, is thick and white with the texture of cottage cheese, and can have a strong or unpleasant smell. Abnormal vaginal discharge can also be accompanied by pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, and blisters or sores.
 Vaginal dryness occurs when the walls of the vagina fail to produce adequate lubrication. Symptoms can include: vaginal itchiness, stinging or soreness, pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), loss of libido, light bleeding following sexual intercourse, and recurring urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Vaginal dryness occurs when the walls of the vagina fail to produce adequate lubrication. Symptoms can include: vaginal itchiness, stinging or soreness, pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), loss of libido, light bleeding following sexual intercourse, and recurring urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Vaginal lubrication is the production of fluid (transudate) by the vaginal wall. It often occurs in response to sexual arousal and helps to reduce friction during sexual intercourse.
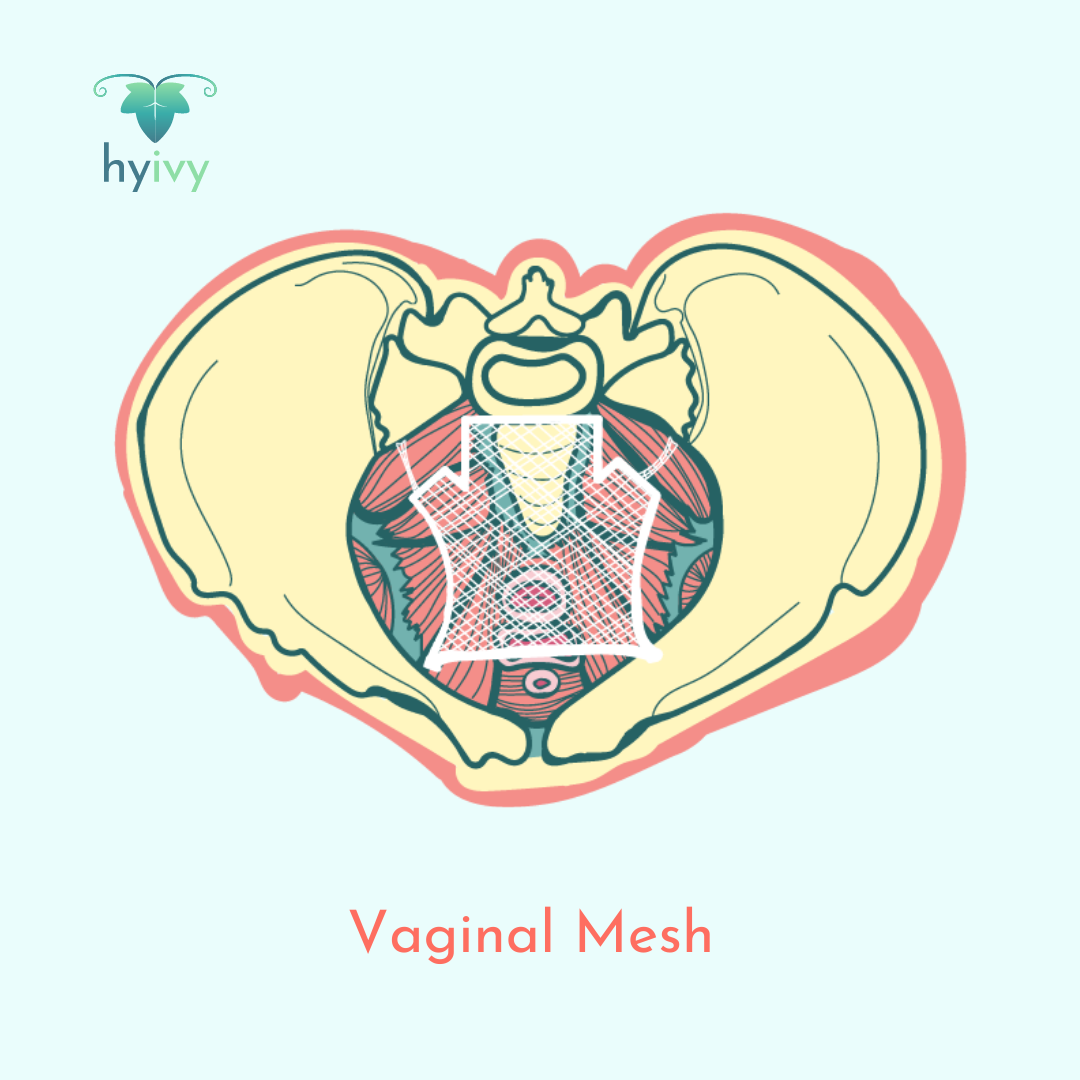 Vaginal mesh (transvaginal mesh) is a net-like medical device used to provide extra support for weakened or damaged vaginal tissues. Vaginal mesh can sometimes be used to repair damage from pelvic organ prolapse or stress urinary incontinence. It can be made out of synthetic or animal products.
Vaginal mesh (transvaginal mesh) is a net-like medical device used to provide extra support for weakened or damaged vaginal tissues. Vaginal mesh can sometimes be used to repair damage from pelvic organ prolapse or stress urinary incontinence. It can be made out of synthetic or animal products.
Vaginal sling procedure is a surgery to help control urinary stress incontinence. A sling made of tissue or synthetic material is passed under the urethra and bladder and attached to the stronger tissues of the lower belly.
Vaginal stenosis occurs when scar tissue forms in the vagina, causing the vagina to become narrower and shorter. This can cause painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), painful pelvic exams, and vaginal dryness. Vaginal stenosis can be caused and made worse by cancer treatments such as radiation and chemotherapy.
Vaginal suppositories are solid, often oval-shaped medications that are meant to be inserted into the vagina. The medication warms to the temperature of the body and becomes liquid in order to be easily absorbed. Vaginal suppositories have a wide range of uses including treatment for: fungal infection (like yeast infections), vaginal dryness, bacterial vaginosis, hormonal or non-hormonal birth control, and to administer hormones like estrogen.
Vaginal vault prolapse is a condition in which the top of the vagina (vaginal cuff) drops down into the vaginal canal or outside of the vagina. It is typically caused by weakness of the pelvic and vaginal tissues and muscles, and can sometimes occur in people who have had a hysterectomy. Symptoms can include: difficulty walking or standing, urinary incontinence, pelvic heaviness, pain in the lower back, and abnormal vaginal bleeding.
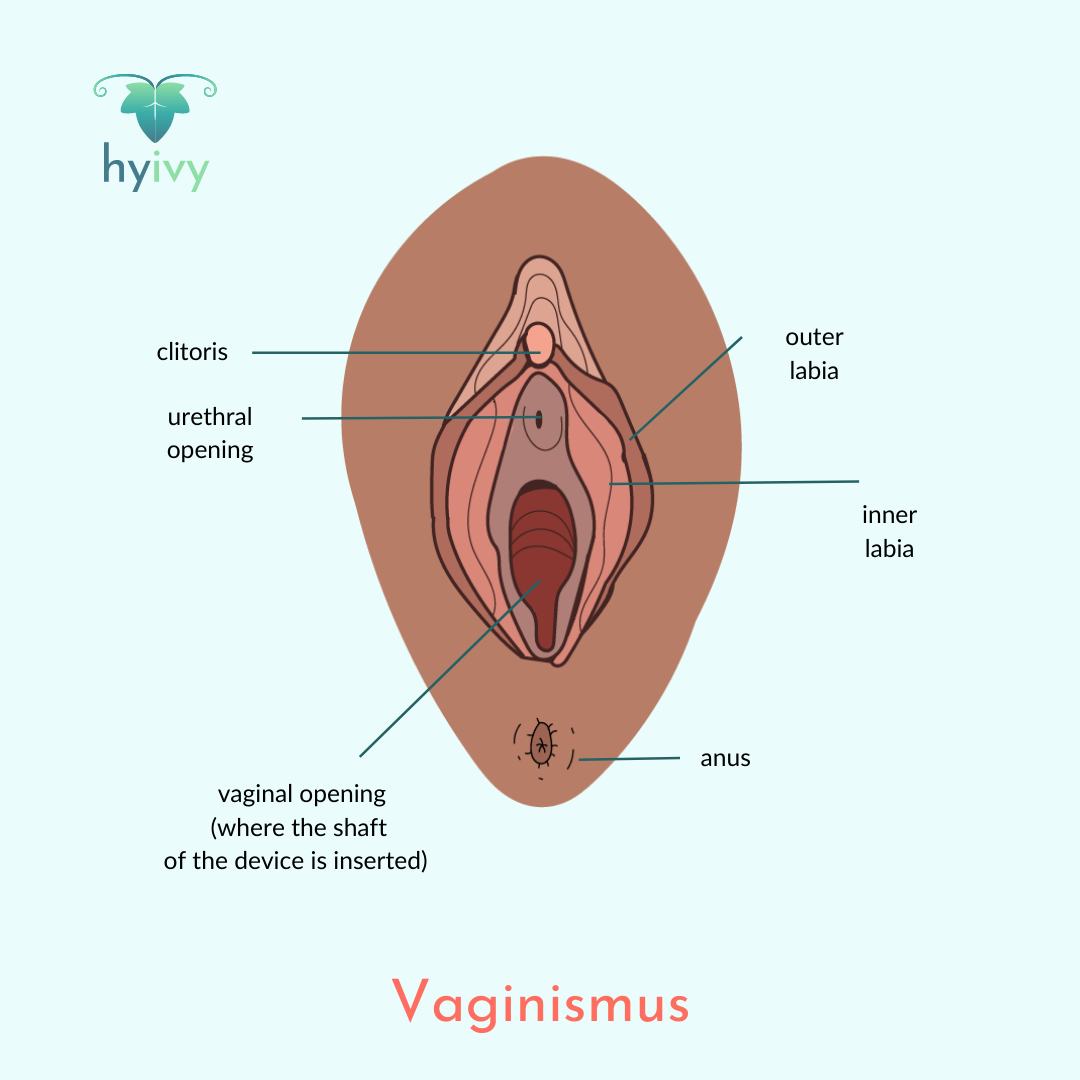 Vaginismus is the involuntary contracting of the muscles surrounding the entrance of the vagina, causing penetration to be painful or impossible. Symptoms can include: pain during penetration of the vagina with a penis, finger, or tampon; stinging, burning, and tightness during sexual intercourse; pain with pelvic or gynecological exams; and avoidance or fear of penetration or sexual intercourse.
Vaginismus is the involuntary contracting of the muscles surrounding the entrance of the vagina, causing penetration to be painful or impossible. Symptoms can include: pain during penetration of the vagina with a penis, finger, or tampon; stinging, burning, and tightness during sexual intercourse; pain with pelvic or gynecological exams; and avoidance or fear of penetration or sexual intercourse.
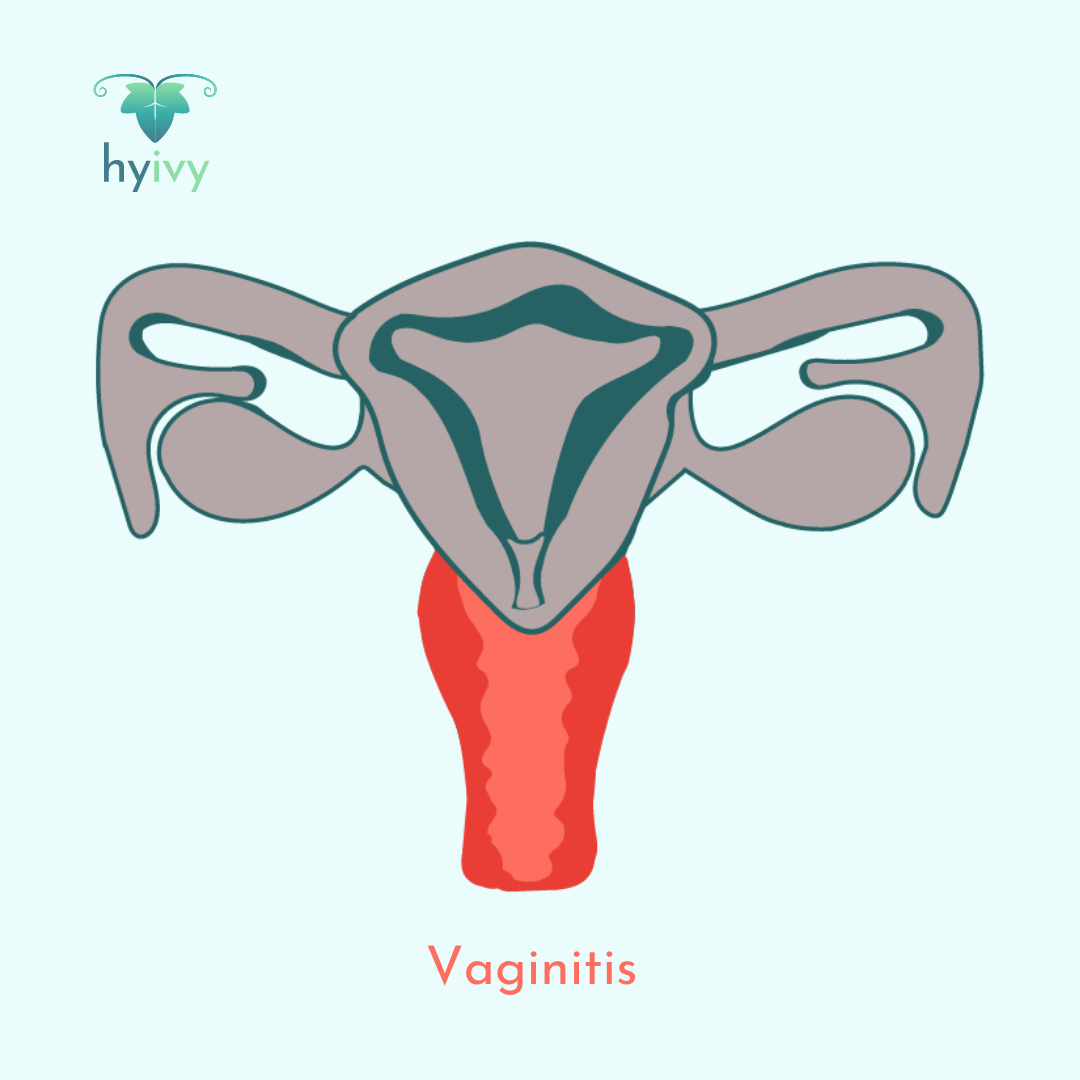 Vaginitis describes any condition that causes inflammation to the vagina, including bacterial vaginosis (BV), vulvovaginal candidiasis (yeast infection), and trichomoniasis (an STI caused by a parasite). Vaginitis can result in abnormal discharge, itching, burning, abnormal odor, and pain.
Vaginitis describes any condition that causes inflammation to the vagina, including bacterial vaginosis (BV), vulvovaginal candidiasis (yeast infection), and trichomoniasis (an STI caused by a parasite). Vaginitis can result in abnormal discharge, itching, burning, abnormal odor, and pain.
Vestibulodynia is pain and discomfort of the vulva, the outer part of your genitalia that surrounds the vaginal opening which consists of the outer labia, inner labia, ureteral opening, clitoris, and mons pubis. Symptoms include: a burning, stinging sensation, sharp pain in this area, pain during vaginal penetration, sexual intercourse, or inserting a tampon, pain with physical activities like bike riding, and a vestibular area that is red or raw.
Vibrators (personal massagers) are objects that vibrate to stimulate the genitals, nipples, and anus. Vibrators come in all shapes and sizes and can be used both inside and outside of the body.
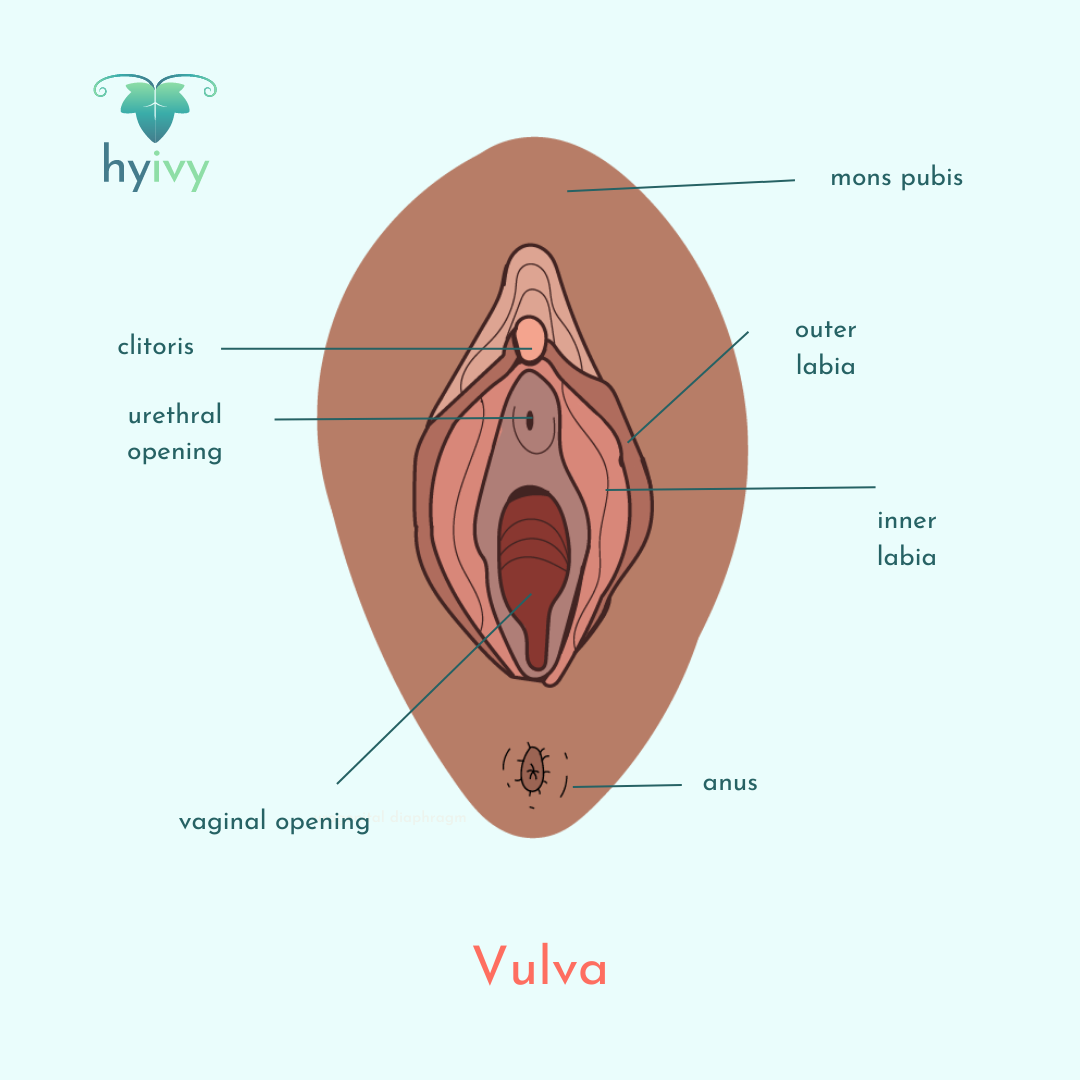
Your vulva is the outer part of your genitalia that surrounds the vaginal opening which consists of the outer labia, inner labia, ureteral opening, clitoris, and mons pubis.
 Vulvodynia is chronic pain around the opening of the vagina lasting for more than three months without other possible causes. The pain can be constant or experienced occasionally. Symptoms can include: itching, burning, soreness, stinging, rawness, painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), or throbbing.
Vulvodynia is chronic pain around the opening of the vagina lasting for more than three months without other possible causes. The pain can be constant or experienced occasionally. Symptoms can include: itching, burning, soreness, stinging, rawness, painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), or throbbing.